Normal Aging Induces Changes in the Brain and Neurodegeneration Progress: Review of the Structural, Biochemical, Metabolic, Cellular, and Molecular Changes
- PMID: 35847660
- PMCID: PMC9281621
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.931536
Normal Aging Induces Changes in the Brain and Neurodegeneration Progress: Review of the Structural, Biochemical, Metabolic, Cellular, and Molecular Changes
Abstract
Aging is accompanied by many changes in brain and contributes to progressive cognitive decline. In contrast to pathological changes in brain, normal aging brain changes have relatively mild but important changes in structural, biochemical and molecular level. Representatively, aging associated brain changes include atrophy of tissues, alteration in neurotransmitters and damage accumulation in cellular environment. These effects have causative link with age associated changes which ultimately results in cognitive decline. Although several evidences were found in normal aging changes of brain, it is not clearly integrated. Figuring out aging related changes in brain is important as aging is the process that everyone goes through, and comprehensive understanding may help to progress further studies. This review clarifies normal aging brain changes in an asymptotic and comprehensive manner, from a gross level to a microscopic and molecular level, and discusses potential approaches to seek the changes with cognitive decline.
Keywords: cellular changes; microscopic changes; neurodegeneration; normal aging; structural changes.
Copyright © 2022 Lee and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
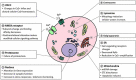
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

