Treating Autoimmune-Related Interstitial Lung Disease With B Cell Depletion
- PMID: 35847798
- PMCID: PMC9279739
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.937561
Treating Autoimmune-Related Interstitial Lung Disease With B Cell Depletion
Abstract
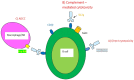
Autoimmune rheumatic diseases may affect vital organs with lung involvement being severe and difficult to treat manifestation. Systemic sclerosis (SSc) commonly affects the lung in the form of interstitial lung disease (ILD). ILD may be also seen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Sjögren's syndrome (SS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), inflammatory myositis (IM), antisynthetase syndrome (AS), and the ANCA-associated vasculitides (AAV). Rituximab (RTX) is an anti-CD20 B lymphocyte depleting mAb, often administered in the treatment of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Although RTX is an off-label treatment for CTD-ILD, there are numerous reports providing data that is effective in improving both pulmonary function tests (PFTs) and chest computed tomography findings consistent with ILD. There are retrospective uncontrolled studies that assess RTX as a treatment of ILD in autoimmune diseases. These studies, apart from one, do not include patients with AAV-ILD. In SSc-ILD, in particular, there are both controlled and uncontrolled studies displaying encouraging results following B cell depletion. In addition, a number of retrospective uncontrolled studies and fewer prospective studies evaluate RTX in connective tissue diseases CTD-ILD. Although RTX is an approved treatment for AAV there are scarce only data focusing on patients with AAV-ILD specifically. The results of a handful of studies comparing treatment of CTD-ILD with RTX to treatment with other agents are in favor of RTX. Results from large, still ongoing controlled trials are awaited to ascertain RTX effects in ILD encountered in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. We review herein the results of the different RTX trials in patients with autoimmune disease-associated with ILD. Despite the heterogeneity of these studies, RTX may be considered an alternative and safe but still off-label treatment for patients with refractory CTD-ILD.
Keywords: B cell depletion; connective tissue diseases; interstitial lung disease; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic sclerosis.
Copyright © 2022 Liossis and Bounia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials