Challenges and Opportunities for Immunoprofiling Using a Spatial High-Plex Technology: The NanoString GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler
- PMID: 35847846
- PMCID: PMC9277770
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.890410
Challenges and Opportunities for Immunoprofiling Using a Spatial High-Plex Technology: The NanoString GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler
Abstract
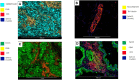
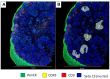
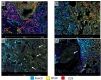
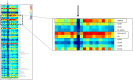
Characterization of the tumor microenvironment through immunoprofiling has become an essential resource for the understanding of the complex immune cell interactions and the assessment of biomarkers for prognosis and prediction of immunotherapy response; however, these studies are often limited by tissue heterogeneity and sample size. The nanoString GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler (DSP) is a platform that allows high-plex profiling at the protein and RNA level, providing spatial and temporal assessment of tumors in frozen or formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded limited tissue sample. Recently, high-impact studies have shown the feasibility of using this technology to identify biomarkers in different settings, including predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy in different tumor types. These studies showed that compared to other multiplex and high-plex platforms, the DSP can interrogate a higher number of biomarkers with higher throughput; however, it does not provide single-cell resolution, including co-expression of biomarker or spatial information at the single-cell level. In this review, we will describe the technical overview of the platform, present current evidence of the advantages and limitations of the applications of this technology, and provide important considerations for the experimental design for translational immune-oncology research using this tissue-based high-plex profiling approach.
Keywords: biomarkers; digital spatial profiling; immune-oncology; pathology; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Hernandez, Lazcano, Serrano, Powell, Kostousov, Mehta, Khan, Lu and Solis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Best Practices for Spatial Profiling for Breast Cancer Research with the GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 4;13(17):4456. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174456. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503266 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Tissue Microarray to GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler : Spatial Transcriptomics Assay with Bioinformatics Analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2880:193-209. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4276-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39900760
-
A user's perspective on GeoMxTM digital spatial profiling.Immunooncol Technol. 2019 May 30;1:11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.iotech.2019.05.001. eCollection 2019 Jul. Immunooncol Technol. 2019. PMID: 35755324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Plex Spatially Resolved RNA and Protein Detection Using Digital Spatial Profiling: A Technology Designed for Immuno-oncology Biomarker Discovery and Translational Research.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2055:563-583. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9773-2_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31502169
-
Region of interest localization, tissue storage time, and antibody binding density-a technical note on the GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler.Immunooncol Technol. 2024 Aug 20;23:100727. doi: 10.1016/j.iotech.2024.100727. eCollection 2024 Sep. Immunooncol Technol. 2024. PMID: 39310847 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping cancer biology in space: applications and perspectives on spatial omics for oncology.Mol Cancer. 2024 Jan 30;23(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01941-z. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38291400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial Transcriptomics Shows a Distinctive Tumour Microenvironment in the Invasive Versus Premalignant Portion of Early Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Exp Dermatol. 2025 Jun;34(6):e70125. doi: 10.1111/exd.70125. Exp Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40462294 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Transcriptomics Unravel the Tissue Complexity of Oral Pathogenesis.J Dent Res. 2024 Dec;103(13):1331-1339. doi: 10.1177/00220345241271934. Epub 2024 Oct 9. J Dent Res. 2024. PMID: 39382116 Review.
-
Quantitative Assessment of Intracellular Effectors and Cellular Response in RAGE Activation.Arch Intern Med Res. 2024;7(2):80-103. doi: 10.26502/aimr.0168. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Arch Intern Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38784044 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal hematopoiesis and its impact on the aging osteo-hematopoietic niche.Leukemia. 2024 May;38(5):936-946. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02226-6. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 38514772 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

