Analysis of ARHGAP4 Expression With Colorectal Cancer Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis
- PMID: 35847897
- PMCID: PMC9278087
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.899837
Analysis of ARHGAP4 Expression With Colorectal Cancer Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis
Abstract
Background: This study aims to analyze the correlation between ARHGAP4 in the expression and clinical characteristics of colorectal cancer (CRC), and the influence of ARHGAP4 expression on the prognosis of CRC, and to evaluate whether ARHGAP4 is a potential prognostic oncotarget for CRC.
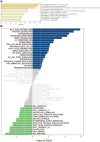
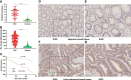
Methods: ARHGAP4 was identified using the Gene Expression Omnibus database through weighted gene coexpression network analysis. Using the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis to perform and analyze the expression and prognosis of ARHGAP4 in CRC. The expression of AGRGAP4 and immune cells was analyzed by the Tumor IMmune Estimation Resource online database. Finally, immunohistochemistry was used to analyze the expression difference and prognosis of ARHGAP4 in CRC and adjacent normal tissues, as well as the relationship between AGRGAP4 expression and clinical features of CRC.
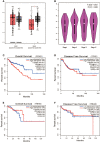
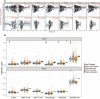
Results: We identified ARHGAP4 that is related to the recurrence of CRC from GSE97781 data. ARHGAP4 has not been reported in CRC. The high expression of ARHGAP4 in select colon adenocarcinoma indicates a poor prognosis by database analysis. In our clinical data results, ARHGAP4 is highly expressed in CRC and lowly expressed in normal tissues adjacent to cancer. Compared with the low-expression group, the high-expression group has a significantly poorer prognosis. In colon cancer, the B-cell, macrophage, neutrophil, and dendritic-cell levels are downregulated after ARHGAP4 gene knockout; the levels of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, neutrophils, and dendritic cells are upregulated after the amplification of the ARHGAP4 gene. In addition, ARHGAP4 expression is related to N,M staging and clinical staging.
Conclusion: ARHGAP4 is highly expressed in CRC, and the high expression of ARHGAP4 has a poor prognosis. The expression of ARHGAP4 in CRC is related to the immune cells such as B cells, CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells. ARHGAP4 is correlated with N,M staging and clinical staging in CRC. ARHGAP4 may be a potential biomarker for the prognosis of CRC.
Keywords: ARHGAP4; CRC; WGCNA; immune; prognostic.
Copyright © 2022 Fu, Pan, Cai, Hu, Zhang and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chi Z, Li Z, Cheng L, Wang C. Comparison of Long-Term Outcomes After Laparoscopic-Assisted and Open Colectomy for Splenic Flexure Cancer. J BUON (2018) 23(2):322–8. - PubMed
-
- Micu BV, Vesa ŞC, Pop TR, Micu CM. Evaluation of Prognostic Factors for 5 Year-Survival After Surgery for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Ital Chir (2020) 91:41–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

