Based on the Development and Verification of a Risk Stratification Nomogram: Predicting the Risk of Lung Cancer-Specific Mortality in Stage IIIA-N2 Unresectable Large Cell Lung Neuroendocrine Cancer Compared With Lung Squamous Cell Cancer and Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35847910
- PMCID: PMC9282874
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.825598
Based on the Development and Verification of a Risk Stratification Nomogram: Predicting the Risk of Lung Cancer-Specific Mortality in Stage IIIA-N2 Unresectable Large Cell Lung Neuroendocrine Cancer Compared With Lung Squamous Cell Cancer and Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study is to predict overall survival (OS) and lung cancer-specific survival (LCSS) in patients with stage IIIA-N2 unresectable lung squamous cell cancer (LUSC), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), and large cell neuroendocrine cancer (LCNEC) by constructing nomograms and to compare risk and prognostic factors affecting survival outcomes in different histological subtypes.
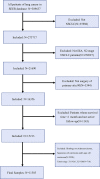
Methods: We included 11,505 unresectable NSCLC patients at stage IIIA-N2 between 2010 and 2015 from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Moreover, competition models and nomograms were developed to predict prognostic factors for OS and LCSS.
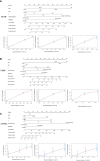
Results: Analysis of the SEER database identified 11,505 NSCLC patients, of whom 5,559 (48.3%) have LUAD, 5,842 (50.8%) have LUSC, and 104 (0.9%) have LCNEC. Overall, both OS and LCSS were significantly better in stage IIIA-N2 unresectable LUAD than in LCNEC, while there was no statistically significant difference between LUSC and LCNEC. Age, gender, T stage, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy were significantly associated with OS rates in LUAD and LUSC. However, chemotherapy was the only independent factor for LCNEC (p < 0.01).From competitive risk models, we found that older age, larger tumors, non-chemotherapy and non-radiotherapy were associated with a increased risk of death from LUAD and LUSC. Unlike prognostic factors for OS, our study showed that both chemotherapy and radiotherapy were all LCNEC-specific survival factors for both LCSS and non-LCSS LCNEC.
Conclusion: Our study reports that unresectable patients with stage IIIA-N2 LCNEC and LUSC have worse LCSS than LUAD. The study's first prognostic nomogram constructed for patients with unresectable stage IIIA-N2 NSCLC can accurately predict the survival of different histological types, which may provide a practical tool to help clinicians assess prognosis and stratify these prognostic risks to determine which patients should be given an optimized individual treatment strategy based on histology.
Keywords: histology; lung cancer-specific survival; nomogram; non-small cell lung cancer; unresectable.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Shen, Shao, Wang, Wang and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with stage III-N2 lung adenocarcinoma based on the SEER database.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 31;12(10):2742-2753. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2757. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37969392 Free PMC article.
-
Double-edged role of radiotherapy in patients with pulmonary large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 19;10(25):6422-6430. doi: 10.7150/jca.32446. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31772675 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence, survival comparison, and novel prognostic evaluation approaches for stage iii-iv pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Apr 5;23(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10797-3. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37020179 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of GLUT1 on the Survival Rate and Immune Cell Infiltration of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta and Bioinformatics Analysis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(2):223-238. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210708115406. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34238200 Review.
-
Are cardiovascular comorbidities always associated with a worse prognosis in patients with lung cancer?Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 23;9:984951. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.984951. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36211566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Smoking Habit and Respiratory Function Predict Patients' Outcome after Surgery for Lung Cancer, Irrespective of Histotype and Disease Stage.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 16;12(4):1561. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041561. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36836096 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing prognostic accuracy: a SEER-based analysis for overall and cancer-specific survival prediction in cervical adenocarcinoma patients.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(19):17027-17037. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05399-2. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37747524 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with stage III-N2 lung adenocarcinoma based on the SEER database.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 31;12(10):2742-2753. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-2757. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37969392 Free PMC article.
-
Oncological outcome and survival predictors of widowed patients with bladder cancer in special populations.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 20;15(1):30638. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13033-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40835628 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the key hub genes linked with lung squamous cell carcinoma by examining the differentially expressed and survival genes.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 Aug 3;299(1):76. doi: 10.1007/s00438-024-02169-8. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39097557
References
-
- Butkiewicz D, Krześniak MK, Gdowicz-Kłosok A, Giglok M, Marszałek-Zé Nczak M, Suwí Nski R. Polymorphisms in EGFR Gene Predict Clinical Outcome in Unresectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Radiotherapy and Platinum-Based Chemoradiotherapy. Int J Mol Sci Artic (2021) 22(11):5605. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115605 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kong C, Zhu X, Shi M, Wang L, Chen C, Tao H, et al. . Survival and Toxicity of Hypofractionated Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy in 4 Gy Fractions for Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys (2020) 107(4):710-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.03.038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hansen RN, Zhang Y, Seal B, Ryan K, Yong C, Darilay A, et al. . Long-Term Survival Trends in Patients With Unresectable Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: A SEER Cancer Registry Analysis. BMC Cancer (2020) 20(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06734-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

