Congenital or Early Developing Neuromuscular Diseases Affecting Feeding, Swallowing and Speech - A Review of the Literature from January 1998 to August 2021
- PMID: 35848032
- PMCID: PMC9535595
- DOI: 10.3233/JND-210772
Congenital or Early Developing Neuromuscular Diseases Affecting Feeding, Swallowing and Speech - A Review of the Literature from January 1998 to August 2021
Abstract
Background: The knowledge about the impact of oral motor impairment in neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) is limited but increasing.
Objective: The aim of this review was to collect and compile knowledge on how muscle weakness in congenital or early developing NMDs directly or indirectly affects feeding, swallowing, speech and saliva control.
Methods: A literature search was performed in PubMed from January 1, 1998, to August 31, 2021. The keywords "feeding", "dysphagia", "swallowing", "dysarthria", "speech", "drooling" and "sialorrhea" were used in combination with "paediatric neuromuscular disease" or specific diagnoses.
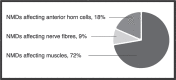
Results: Sixty-five studies were selected for the review, 33 focused on feeding and swallowing, 11 on speech, four on a combination of feeding, swallowing, saliva control or speech and 17 general descriptions. Most of the studies reported on patients with a disorder affecting muscles. These studies show that muscle weakness and impaired motility affecting the muscles innervated by the cranial nerves may influence feeding, swallowing, and speech, and that respiratory function, general health and neurodevelopmental delay also influence these functions. Feeding impairment and breathing difficulties are common in NMDs. Lifesaving interventions such as tube feeding and ventilatory support are common in severe cases.
Conclusions: Feeding impairment, dysphagia and dysarthria are prevalent in NMDs with congenital or early age of onset. Feeding and swallowing has been studied more than speech and saliva control. More children with NMD survive thanks to new treatment options and it is therefore urgent to follow up how these therapies may impact the development of feeding, swallowing, and speech.
Keywords: Neuromuscular disease; dysarthria; dysphagia; feeding; speech; swallowing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Deenen JC, Horlings CG, Verschuuren JJ, Verbeek AL, van Engelen BG, The epidemiology of neuromuscular disorders: A comprehensive overview of the literature. J Neuromuscul Dis 2015;2(1):73–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical