Early steps of embryo implantation are regulated by exchange of extracellular vesicles between the embryo and the endometrium
- PMID: 35848638
- PMCID: PMC12166289
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202200677R
Early steps of embryo implantation are regulated by exchange of extracellular vesicles between the embryo and the endometrium
Abstract
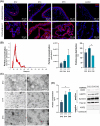
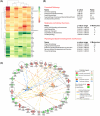
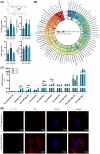
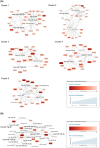
In early pregnancy, as the embryo arrives in the uterus, intensive communication between the embryo and uterus begins. Hundreds of molecules are known to be involved, but despite numerous findings, full understanding of the complexity of the embryo-maternal dialog remains elusive. Recently, extracellular vesicles, nanoparticles able to transfer functionally active cargo between cells, have emerged as important players in cell-cell communication, and as such, they have gained great attention over the past decade also in reproductive biology. Here, we use a domestic animal model (Sus scrofa) with an epitheliochorial, superficial type of placentation because of its advantage in studding uterine luminal fluid extracellular vesicles. We show that during early pregnancy, the uterine lumen is abundant with extracellular vesicles that carry a plethora of miRNAs able to target genes involved in embryonic and organismal development. These extracellular vesicles, upon the delivery to primary trophoblast cells, affect genes governing development as well as cell-to-cell signaling and interactions, consequently having an impact on trophoblast cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. We conclude that the exchange of a unique population of extracellular vesicles and their molecular cargo at the maternal-embryo interface is the key to the success of embryo implantation and pregnancy.
Keywords: embryo; extracellular vesicles; implantation; invasion; miRNA; migration; pregnancy; proliferation; transcriptome; trophoblast.
© 2022 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Van Soom A, Wydooghe E, Heras S, et al. Alternative models for the study of embryo–maternal cross‐talk and signaling molecules from fertilisation to implantation. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2011;23:iii‐v. - PubMed
-
- Bazer FW, Geisert RD, Thatcher WW, Roberts RM. The establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. In: Cole DJA, Foxcroft GR, eds. Control of Pig Reproduction. Butterworth Scientific; 1982:227‐252.
-
- Flint APF, Saunders PTK, Ziecik AJ. Blastocyt‐endometrium interactions and their significance in embryonic mortality. In: Cole DJA, Foxcroft GR, eds. Control of Pig Reproduction. Butterworth Scientific; 1982:253‐275.
-
- Wilcox AJ, Weinberg CR, O'Connor JF, et al. Incidence of early loss of pregnancy. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:189‐194. - PubMed
-
- Hakim RB, Gray RH, Zacur H. Infertility and early pregnancy loss. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995;172:1510‐1517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

