Effect of fasting on cancer: A narrative review of scientific evidence
- PMID: 35848874
- PMCID: PMC9530862
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15492
Effect of fasting on cancer: A narrative review of scientific evidence
Abstract
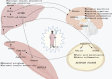
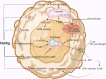
Emerging evidence suggests that fasting could play a key role in cancer treatment by fostering conditions that limit cancer cells' adaptability, survival, and growth. Fasting could increase the effectiveness of cancer treatments and limit adverse events. Yet, we lack an integrated mechanistic model for how these two complicated systems interact, limiting our ability to understand, prevent, and treat cancer using fasting. Here, we review recent findings at the interface of oncology and fasting metabolism, with an emphasis on human clinical studies of intermittent fasting. We recommend combining prolonged periodic fasting with a standard conventional therapeutic approach to promote cancer-free survival, treatment efficacy and reduce side effects in cancer patients.
Keywords: cancer; diet; fasting; intermittent fasting; oncology; review.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Clifton KK, Ma CX, Fontana L, Peterson LL. Intermittent fasting in the prevention and treatment of cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:527‐546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

