Elucidation of structure-function relationships in Methanocaldococcus jannaschii RNase P, a multi-subunit catalytic ribonucleoprotein
- PMID: 35848927
- PMCID: PMC9371926
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac595
Elucidation of structure-function relationships in Methanocaldococcus jannaschii RNase P, a multi-subunit catalytic ribonucleoprotein
Abstract
RNase P is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) that catalyzes removal of the 5' leader from precursor tRNAs in all domains of life. A recent cryo-EM study of Methanocaldococcus jannaschii (Mja) RNase P produced a model at 4.6-Å resolution in a dimeric configuration, with each holoenzyme monomer containing one RNase P RNA (RPR) and one copy each of five RNase P proteins (RPPs; POP5, RPP30, RPP21, RPP29, L7Ae). Here, we used native mass spectrometry (MS), mass photometry (MP), and biochemical experiments that (i) validate the oligomeric state of the Mja RNase P holoenzyme in vitro, (ii) find a different stoichiometry for each holoenzyme monomer with up to two copies of L7Ae, and (iii) assess whether both L7Ae copies are necessary for optimal cleavage activity. By mutating all kink-turns in the RPR, we made the discovery that abolishing the canonical L7Ae-RPR interactions was not detrimental for RNase P assembly and function due to the redundancy provided by protein-protein interactions between L7Ae and other RPPs. Our results provide new insights into the architecture and evolution of RNase P, and highlight the utility of native MS and MP in integrated structural biology approaches that seek to augment the information obtained from low/medium-resolution cryo-EM models.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

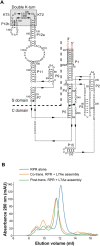
 ) or without (blue line,
) or without (blue line,  ) the addition of Mja L7Ae during the in vitro transcription reaction, or the purified Mja RPR assembled with Mja L7Ae post-transcription (green line,
) the addition of Mja L7Ae during the in vitro transcription reaction, or the purified Mja RPR assembled with Mja L7Ae post-transcription (green line,  ) were separately loaded onto the Superdex 200 increase 10/30 GL column (GE Healthcare) at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Eluent was monitored for absorbance at 280 nm. Fractions corresponding to the main peak were collected and concentrated for native MS analysis.
) were separately loaded onto the Superdex 200 increase 10/30 GL column (GE Healthcare) at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. Eluent was monitored for absorbance at 280 nm. Fractions corresponding to the main peak were collected and concentrated for native MS analysis.
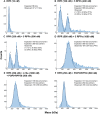

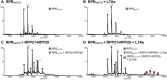
References
-
- Liu S., Li B., Liang Q., Liu A., Qu L., Yang J.. Classification and function of RNA–protein interactions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2020; 11:e1601. - PubMed
-
- Altman S. Liu F., Altman S.. Ribonuclease P. 2010; NY: Springer; 1–15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

