Efficacy of Sishen Wan on dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis and its effect on toll-like receptor 2/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway
- PMID: 35848973
- PMCID: PMC9924653
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220608.001
Efficacy of Sishen Wan on dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis and its effect on toll-like receptor 2/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the therapeutic effect of Sishen Wan (, SSW) on ulcerative colitis (UC) induced by dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid and its effect on toll-like receptor 2/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4/nuclear factor-κB (TLR2/IRAK4/NF-κB) sig-naling pathway in colonic tissue.
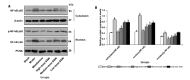
Methods: In this study, 120 Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into blank and model groups. The experimental UC model in rats was established by subcutaneous injection of hydrocortisone + senna gavage for 21 d + dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS)/ ethanol solution enema. The successful model rats were randomly divided into the model group; mesalazine (0.36 g/kg) group; and high-, medium-, and low- dose SSW (24, 12, and 6 g/kg) groups. The model and blank groups were gavaged with equal volumes of distilled water once a day for 21 d. The general condition of the rats was observed, and the body mass, fecal properties, and occult blood were recorded for calculating the disease activity index (DAI) score. The colonic tissue of the rats was collected, and its general morphology and pathological form were noted for obtaining the colonic mucosal injury index (CMDI) score. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to view the pathological changes of the colon tissue in each group, apoptosis of the cells was detected using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling staining, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to measure the expressions of TLR2, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88), IRAK4, and NF-κB p65 mRNA in the colon tissue. The expressions of TLR2, MyD88, IRAK4, and NF-κB p65 protein were detected using western blotting and immunohistochemistry assay, and the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in the colon tissue were determined using enzyme linked immunosorbent assay.
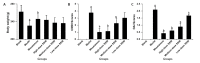
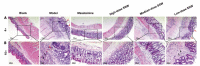
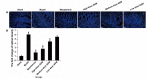
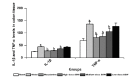
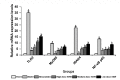
Results: Compared with the blank group, the general condition of the model group was relatively poor. The DAI and CMDI scores of the model group increased significantly (< 0.01), the glands and intestinal mucosa disappeared partially, and several inflammatory cells infiltrated and gathered in the mucosal layer and base layer of the rats in the model group. Furthermore, the cell apoptosis and expression levels of TLR2, MyD88, IRAK4, and NF-κB p65 mRNA and protein in the colon tissue of rats in the model group increased significantly (< 0.01). The levels of IL-1β and TNF-α increased significantly in the colon tissue of rats in the model group (< 0.01). After treatment with SSW, compared with the model group, the general condition of the UC rats improved. Moreover, the DAI and CMDI scores of the UC rats decreased significantly (< 0.05), and the pathological changes in the colon tissue of the UC rats tended to be normal. The cell apoptosis and expression levels of TLR2, MyD88, IRAK4, and NF-κB p65 mRNA and protein in the colon tissue of the UC rats decreased gradually ( < 0.01), and the levels of IL-1β and TNF-α decreased significantly (< 0.01).
Conclusion: SSW can improve the general condition and alleviate the intestinal mucosal injury of UC model rats. Additionally, SSW can inhibit the TLR2/IRAK4/ NF-κB signaling pathway, but further studies are required to confirm it.
Keywords: NF-kappa B; Sishen Wan; colitis, ulcerative; interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases; signal transduction; therapeutic uses; toll-like receptor 2.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Moxibustion with seed-size moxa cones alleviates colonic injury in mice with ulcerative colitis by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024 Aug 25;49(8):836-844. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240189. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2024. PMID: 39318313 Chinese, English.
-
[Effect and mechanism of alkaloids from Portulacae Herba on ulcerative colitis in mice based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Feb;50(4):874-881. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20241009.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40350807 Chinese.
-
[Electroacupuncture of "Shangjuxu"(ST37) and "Tianshu"(ST25) reduces colonic injury by suppressing NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling in rats with ulcerative colitis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Apr 25;47(4):314-20. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210361. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35486010 Chinese.
-
Effects of Toll-like receptor 1 and 2 agonist Pam3CSK4 on uveal melanocytes and relevant experimental mouse model.Exp Eye Res. 2024 Feb;239:109749. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2023.109749. Epub 2023 Dec 17. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38113956 Review.
-
Exploring the influence of non-coding RNAs on NF-κB signaling pathway regulation in ulcerative colitis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117390. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117390. Epub 2024 Sep 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39243424 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Gut-Kidney Axis in Diarrhea with Kidney-Yang Deficiency Syndrome: The Role of Sishen Pills in Regulating TMAO-Mediated Inflammatory Response.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jun 20;30:e944185. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944185. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38898640 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation Reveal Sishen Pill's Efficacy in Treating NSAID-Induced Small Intestinal Ulcers.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Mar 19;19:2035-2050. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S502193. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40124554 Free PMC article.
-
Sishen Pill and its active phytochemicals in treating inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer: an overview.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1375585. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1375585. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38650627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRAK4 Targeting: A Breakthrough Approach to Combat Hidradenitis Suppurativa.Biologics. 2025 Jun 30;19:387-397. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S525106. eCollection 2025. Biologics. 2025. PMID: 40621493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eisenstein M. Ulcerative colitis: towards remission. Nature 2018; 563: S33. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi T, Siegmund B, Le Berre C, et al.. Ulcerative colitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020; 6: 73. - PubMed
-
- Du L, Ha C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2020; 49: 643-54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
