Efficacy and safety of a sequential treatment with clearing heat and eliminating phlegm and tonifying and activating blood circulation in treating acute ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35848977
- PMCID: PMC9924680
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220617.003
Efficacy and safety of a sequential treatment with clearing heat and eliminating phlegm and tonifying and activating blood circulation in treating acute ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the short-term efficacy and safety outcomes following a sequential treatment with clearing heat and eliminating phlegm (CHEP) formula and tonifying Qi and activating blood circulation (TQABC) formula in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) within a 72 h time window.
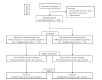
Methods: In this randomized, multicenter, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial, 500 participants will be randomly assigned in a ratio of 1∶1 to the CHEP+ TQABC group or control group. In addition to guideline-based standard medical care, participants in the treatment group will receive the CHEP formula for the first 5 consecutive days followed by the TQABC formula for another 10 consecutive days, while those in the control group will receive CHEP formula placebo and TQABC formula placebo consecutively. The primary outcome measure will be the comparison of the change in the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score from baseline to 15 days after randomization. The secondary outcome measures will include the scores on the modified Rankin Scale, Barthel Index, Patient-Reported Outcomes, TCM symptom pattern (Zheng-hou) evaluation Scale, and the incidence of in-hospital complications. Safety assessment will include the physical examination, laboratory detection, any adverse events or serious adverse events, and the proportion of any complications during hospitalization.
Discussion: The results of this study will provide objective and scientific data with which to assess the efficacy and safety of a sequential treatment based on "integrating disease and symptom pattern" for patients with AIS.
Keywords: clearing heat and eliminating phlegm; clinical protocols; randomized controlled trial; stroke; tonifying and activating blood circulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (inactivated, Vero cell): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Apr 13;22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05180-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33849629 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Y-2 sublingual tablet for patients with acute ischaemic stroke: protocol of a phase III randomised double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre trial.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2024 Feb 27;9(1):90-95. doi: 10.1136/svn-2022-002014. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37308251 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Panax Notoginseng Saponins (Xueshuantong) in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke (EXPECT) Trial: Rationale and Design.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 22;12:648921. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.648921. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33967788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang WZ, Jiang B, Sun HX, et al.. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation 2017; 135: 759-71. - PubMed
-
- Jiang M, Lu C, Zhang C, et al.. Syndrome differentiation in modern research of traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 2012; 140: 634-42. - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Li MQ, Li Y, et al.. Exploring Chinese medicine and Western Medicine group modules in acute phase of ischemic stroke disease. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2018; 43: 618-26. - PubMed
-
- Yeh ML, Chiu WL, Wang YJ, Lo C. An investigation of the use of Traditional Chinese Medicine and complementary and alternative medicine in stroke patients. Holist Nurs Pract 2017; 31: 400-7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical