Synergistic Effects of Natural Product Combinations in Protecting the Endothelium Against Cardiovascular Risk Factors
- PMID: 35849068
- PMCID: PMC9297466
- DOI: 10.1177/2515690X221113327
Synergistic Effects of Natural Product Combinations in Protecting the Endothelium Against Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Abstract
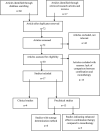
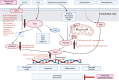
Endothelial dysfunction is an early hallmark of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Monotherapies are limited due to the complex, multifactorial pathways. The multi-component and multi-targeted approach of natural products have the potential to manage CVDs.This review aims to provide a comprehensive insight into the synergistic mechanism of natural product combinations in protecting the endothelium against various cardiovascular risk factors.Databases (PubMed, MEDLINE and EMBASE) and Google Scholar were searched, and studies in English published between January 2000 and February 2022 were collated. Clinical and pre-clinical studies of natural product combinations with or without pharmaceutical medicines, compared with monotherapy and/or proposing the underlying mechanism in protecting endothelial function, were included.Four clinical studies demonstrated that natural product combinations or natural product-pharmaceutical combinations improved endothelial function. This was associated with multi-targeted effects or improved absorption of the active substances in the body. Seventeen preclinical studies showed that natural product combinations produced synergistic (demonstrated by combination index or Bliss independence model) or enhanced effects in protecting the endothelium against hyperlipidemia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, platelet activation, oxidative stress and hyperhomocysteinemia. The molecular targets included reactive oxygen species, Nrf2-HO-1, p38MAPK, P13K/Akt and NF-κB.Thus, the current available evidence of natural product combinations in targeting endothelial dysfunction is predominantly from preclinical studies. These have demonstrated synergistic/enhanced pharmacological activities and proposed associated mechanisms. However, evidence from larger, well-designed clinical trials remains weak. More cohesion is required between preclinical and clinical data to support natural product combinations in preventing or slowing the progression of CVDs.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; combination index; endothelial dysfunction; natural products; synergy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical