Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Status and Future Perspectives: A State-of-the-Art Review
- PMID: 35849321
- PMCID: PMC9510088
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-022-00475-4
Artificial Intelligence in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Status and Future Perspectives: A State-of-the-Art Review
Abstract
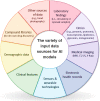
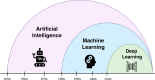
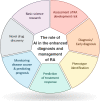
Investigation of the potential applications of artificial intelligence (AI), including machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques, is an exponentially growing field in medicine and healthcare. These methods can be critical in providing high-quality care to patients with chronic rheumatological diseases lacking an optimal treatment, like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which is the second most prevalent autoimmune disease. Herein, following reviewing the basic concepts of AI, we summarize the advances in its applications in RA clinical practice and research. We provide directions for future investigations in this field after reviewing the current knowledge gaps and technical and ethical challenges in applying AI. Automated models have been largely used to improve RA diagnosis since the early 2000s, and they have used a wide variety of techniques, e.g., support vector machine, random forest, and artificial neural networks. AI algorithms can facilitate screening and identification of susceptible groups, diagnosis using omics, imaging, clinical, and sensor data, patient detection within electronic health record (EHR), i.e., phenotyping, treatment response assessment, monitoring disease course, determining prognosis, novel drug discovery, and enhancing basic science research. They can also aid in risk assessment for incidence of comorbidities, e.g., cardiovascular diseases, in patients with RA. However, the proposed models may vary significantly in their performance and reliability. Despite the promising results achieved by AI models in enhancing early diagnosis and management of patients with RA, they are not fully ready to be incorporated into clinical practice. Future investigations are required to ensure development of reliable and generalizable algorithms while they carefully look for any potential source of bias or misconduct. We showed that a growing body of evidence supports the potential role of AI in revolutionizing screening, diagnosis, and management of patients with RA. However, multiple obstacles hinder clinical applications of AI models. Incorporating the machine and/or deep learning algorithms into real-world settings would be a key step in the progress of AI in medicine.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Autoimmune diseases; Deep learning; Diagnosis; Imaging; Machine learning; Natural language processing; Precision medicine; Rheumatoid arthritis; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Artificial intelligence. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/artificial%20intelligence. Accessed 15 Feb 2022.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

