Use of Facial Morphology to Determine Nutritional Status in Older Adults: Opportunities and Challenges
- PMID: 35849429
- PMCID: PMC9345026
- DOI: 10.2196/33478
Use of Facial Morphology to Determine Nutritional Status in Older Adults: Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract
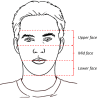
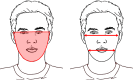
Undiagnosed malnutrition is a significant problem in high-income countries, which can reduce the quality of life of many individuals, particularly of older adults. Moreover, it can also inflate the costs of existing health care systems because of the many metabolic complications that it can cause. The current methods for assessing malnutrition can be cumbersome. A trained practitioner must be present to conduct an assessment, or patients must travel to facilities with specialized equipment to obtain their measurements. Therefore, digital health care is a possible way of closing this gap as it is rapidly gaining traction as a scalable means of improving efficiency in the health care system. It allows for the remote monitoring of nutritional status without requiring the physical presence of practitioners or the use of advanced medical equipment. As such, there is an increasing interest in expanding the range of digital applications to facilitate remote monitoring and management of health issues. In this study, we discuss the feasibility of a novel digital remote method for diagnosing malnutrition using facial morphometrics. Many malnutrition screening assessments include subjective assessments of the head and the face. Facial appearance is often used by clinicians as the first point of qualitative indication of health status. Hence, there may be merit in quantifying these subtle but observable changes using facial morphometrics. Modern advancements in artificial intelligence, data science, sensors, and computing technologies allow facial features to be accurately digitized, which could potentially allow these previously intuitive assessments to be quantified. This study aims to stimulate further discussion and discourse on how this emerging technology can be used to provide real-time access to nutritional status. The use of facial morphometrics extends the use of currently available technology and may provide a scalable, easily deployable solution for nutritional status to be monitored in real time. This will enable clinicians and dietitians to keep track of patients remotely and provide the necessary intervention measures as required, as well as providing health care institutions and policy makers with essential information that can be used to inform and enable targeted public health approaches within affected populations.
Keywords: 3D scans; digital health; digital nutrition; facial morphology; facial recognition; malnutrition; mobile phone; public health nutrition; telemonitoring.
©Wesley Tay, Rina Quek, Bhupinder Kaur, Joseph Lim, Christiani Jeyakumar Henry. Originally published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance (https://publichealth.jmir.org), 18.07.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Advancing Nutritional Status Classification With Hybrid Artificial Intelligence: A Novel Methodological Approach.Brain Behav. 2025 May;15(5):e70548. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70548. Brain Behav. 2025. PMID: 40356452 Free PMC article.
-
Malnutrition in older adults - urgent need for action: a plea for improving the nutritional situation of older adults.Gerontology. 2013;59(4):328-33. doi: 10.1159/000346142. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Gerontology. 2013. PMID: 23406648 Review.
-
Screening for Malnutrition in Older People.Clin Geriatr Med. 2015 Aug;31(3):429-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 May 13. Clin Geriatr Med. 2015. PMID: 26195101 Review.
-
Assessing the feasibility of a mobile health-supported clinical decision support system for nutritional triage in oncology outpatients using Arden Syntax.Artif Intell Med. 2018 Nov;92:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Artif Intell Med. 2018. PMID: 26563776
Cited by
-
Advancing the Understanding of Malnutrition in the Elderly Population: Current Insights and Future Directions.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 31;16(15):2502. doi: 10.3390/nu16152502. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-assisted facial analysis in healthcare: From disease detection to comprehensive management.Patterns (N Y). 2025 Feb 4;6(2):101175. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2025.101175. eCollection 2025 Feb 14. Patterns (N Y). 2025. PMID: 40041850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Facial Proportions in Stunted and Non-Stunted Children Aged 7-72 Months: A Cross-Sectional Study in Bandung, Indonesia.Children (Basel). 2025 Aug 7;12(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/children12081037. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868489 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a point-of-care nursing mobile tool to guide the diagnosis of malnutrition in hospitalized adult patients: a multicenter, prospective cohort study.MedComm (2020). 2024 Apr 10;5(4):e526. doi: 10.1002/mco2.526. eCollection 2024 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38606361 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Malnutrition: A Systematic Literature Review.Adv Nutr. 2024 Sep;15(9):100264. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2024.100264. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Adv Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38971229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Visvanathan R. Under-nutrition in older people: a serious and growing global problem! J Postgrad Med. 2003;49(4):352–60. http://www.jpgmonline.com/article.asp?issn=0022-3859;year=2003;volume=49... - PubMed
-
- Ahmed T, Haboubi N. Assessment and management of nutrition in older people and its importance to health. Clin Interv Aging. 2010 Aug 09;5:207–16. doi: 10.2147/cia.s9664. https://www.dovepress.com/articles.php?article_id=4939 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wysokiński A, Sobów T, Kłoszewska I, Kostka T. Mechanisms of the anorexia of aging-a review. Age (Dordr) 2015 Aug;37(4):9821. doi: 10.1007/s11357-015-9821-x. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/26232135 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sampson G. Weight loss and malnutrition in the elderly--the shared role of GPs and APDs. Aust Fam Physician. 2009 Jul;38(7):507–10. http://www.racgp.org.au/afp/200907/32621 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

