Fasciola hepatica Cathepsin L Zymogens: Immuno-Proteomic Evidence for Highly Immunogenic Zymogen-Specific Conformational Epitopes to Support Diagnostics Development
- PMID: 35849550
- PMCID: PMC9361350
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00299
Fasciola hepatica Cathepsin L Zymogens: Immuno-Proteomic Evidence for Highly Immunogenic Zymogen-Specific Conformational Epitopes to Support Diagnostics Development
Abstract
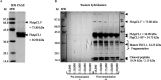
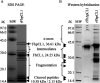
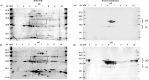
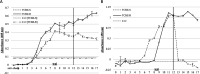
Fasciola hepatica, the common liver fluke and causative agent of zoonotic fasciolosis, impacts on food security with global economic losses of over $3.2 BN per annum through deterioration of animal health, productivity losses, and livestock death and is also re-emerging as a foodborne human disease. Cathepsin proteases present a major vaccine and diagnostic target of the F. hepatica excretory/secretory (ES) proteome, but utilization in diagnostics of the highly antigenic zymogen stage of these proteins is surprisingly yet to be fully exploited. Following an immuno-proteomic investigation of recombinant and native procathepsins ((r)FhpCL1), including mass spectrometric analyses (DOI: 10.6019/PXD030293), and using counterpart polyclonal antibodies to a recombinant mutant procathepsin L (anti-rFhΔpCL1), we have confirmed recombinant and native cathepsin L zymogens contain conserved, highly antigenic epitopes that are conformationally dependent. Furthermore, using diagnostic platforms, including pilot serum and fecal antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests, the diagnostic capacities of cathepsin L zymogens were assessed and validated, offering promising efficacy as markers of infection and for monitoring treatment efficacy.
Keywords: cathepsin; diagnostics; fasciolosis; recombinant; triclabendazole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dalton J. P.; Skelly P.; Halton D. W. Role of the tegument and gut in nutrient uptake by parasitic platyhelminths. Can. J. Zool. 2004, 82, 211–232. 10.1139/z03-213. - DOI
-
- Dalton J. P.; Neill S. O.; Stack C.; Collins P. R.; Walshe A.; Sekiya M.; et al. Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L-like proteases: biology, function, and potential in the development of first generation liver fluke vaccines. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1173–1181. 10.1016/S0020-7519(03)00171-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
Sep 30
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

