Deletion of SM22α disrupts the structure and function of caveolae and T-tubules in cardiomyocytes, contributing to heart failure
- PMID: 35849583
- PMCID: PMC9292107
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271578
Deletion of SM22α disrupts the structure and function of caveolae and T-tubules in cardiomyocytes, contributing to heart failure
Abstract
Aims: Smooth muscle 22-alpha (SM22α) is an actin-binding protein that plays critical roles in mediating polymerization of actin filaments and stretch sensitivity of cytoskeleton in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Multiple lines of evidence indicate the existence of SM22α in cardiomyocytes. Here, we investigated the effect of cardiac SM22α on the membrane architecture and functions of cardiomyocytes to pressure overload.
Methods: SM22α knock-out (KO) mice were utilized to assess the role of SM22α in the heart. Echocardiography was used to evaluate cardiac function, transverse aortic constriction (TAC) was used to induce heart failure, cell shortening properties were measured by IonOptix devices in intact cardiomyocytes, Ca2+ sensitivity of myofilaments was measured in permeabilized cardiomyocytes. Confocal microscopy, electron microscopy, western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP), Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) techniques were used to perform functional and structural analysis.
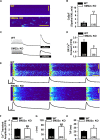
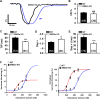
Results: SM22α ablation did not alter cardiac function at baseline, but mRNA levels of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and β-myosin heavy chain (β-MHC) were increased significantly compared with wild type (WT) controls. The membrane architecture was severely disrupted in SM22α KO cardiomyocytes, with disassembly and flattening of caveolae and disrupted T-tubules. Furthermore, SM22α was co-immunoprecipitated with caveolin-3 (Cav3), and the interaction between Cav3 and actin was significantly reduced in SM22α KO cells. SM22α KO cardiomyocytes displayed asynchronized SR Ca2+ release, significantly increased Ca2+ spark frequency. Additionally, the kinetics of sarcomere shortening was abnormal, accompanied with increased sensitivity and reduced maximum response of myofilaments to Ca2+ in SM22α KO cardiomyocytes. SM22α KO mice were more prone to heart failure after TAC.
Conclusions: Our findings identified that SM22α may be required for the architecture and function of caveolae and T-tubules in cardiomyocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Lees-Miller JP, Heeley DH, Smillie LB, Kay CM. Isolation and characterization of an abundant and novel 22-kDa protein (SM22) from chicken gizzard smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987;262(7):2988–2993.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

