Treatment with a VEGFR-2 antibody results in intra-tumor immune modulation and enhances anti-tumor efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in syngeneic murine tumor models
- PMID: 35849586
- PMCID: PMC9292077
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268244
Treatment with a VEGFR-2 antibody results in intra-tumor immune modulation and enhances anti-tumor efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in syngeneic murine tumor models
Abstract
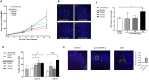
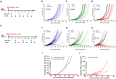
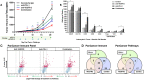
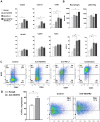
Prolonged activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) due to mis-regulation of the VEGF pathway induces aberrant blood vessel expansion, which supports growth and survival of solid tumors. Therapeutic interventions that inhibit the VEGFR-2 pathway have therefore become a mainstay of cancer treatment. Non-clinical studies have recently revealed that blockade of angiogenesis can modulate the tumor microenvironment and enhance the efficacy of concurrent immune therapies. Ramucirumab is an FDA-approved anti-angiogenic antibody that inhibits VEGFR-2 and is currently being evaluated in clinical studies in combination with anti-programmed cell death (PD-1) axis checkpoint inhibitors (pembrolizumab, durvalumab, or sintilimab) across several cancer types. The purpose of this study is to establish a mechanistic basis for the enhanced activity observed in the combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and PD-1-axis pathways. Pre-clinical studies were conducted in murine tumor models known to be responsive to anti-PD-1 axis therapy, using monoclonal antibodies that block mouse VEGFR-2 and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). Combination therapy resulted in enhanced anti-tumor activity compared to anti-PD-L1 monotherapy. VEGFR-2 blockade at early timepoints post-anti-PD-L1 therapy resulted in a dose-dependent and transient enhanced infiltration of T cells, and establishment of immunological memory. VEGFR-2 blockade at later timepoints resulted in enhancement of anti-PD-L1-driven immune cell infiltration. VEGFR-2 and PD-L1 monotherapies induced both unique and overlapping patterns of immune gene expression, and combination therapy resulted in an enhanced immune activation signature. Collectively, these results provide new and actionable insights into the mechanisms by which concurrent VEGFR-2 and PD-L1 antibody therapy leads to enhanced anti-tumor efficacy.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.L. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work and is currently an employee of Regeneron. N.A. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. M.O.M. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. J.R.M. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. I.I. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work and is currently an employee of Astra Zeneca. Q.L. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. E.R.R. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. M.B. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work and is currently an employee of Sanofi, US. T.N.D. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. G.H. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. M.K. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work, and currently Managing Director of Next Pillar Consulting, LLC. M.K. reports stock ownership as a result of employment or advisory roles in: ArsenalBio, Immunai, Cue Biopharma, Nanocell therapeutics, IMV inc., SentiBio, AdicetBio, Orange Grove Bio. Issued patents in the field of cell therapy, licensed by the University of Pennsylvania to Novartis corporation, resulting in royalty distributions. R.N. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work and is currently an employee of Bristol-Myers Squibb. O.P. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly. B.P. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work and is currently an employee of OncXerna Therapeutics, Inc. B.P. reports support for attending meetings and/or travel and stock/stock options from OncXerna Therapeutics, Inc. D.A.S. employee and shareholder of Eli Lilly at the time of this work and is currently an employee of Pfizer. D.A.S. reports support for attending meetings and/or travel from Pfizer Inc (employee of Pfizer). This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Augmenting Anticancer Immunity Through Combined Targeting of Angiogenic and PD-1/PD-L1 Pathways: Challenges and Opportunities.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 5;11:598877. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.598877. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33250900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Programmed Death Receptor-1 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 Blockade Promotes Vascular Normalization and Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepatology. 2020 Apr;71(4):1247-1261. doi: 10.1002/hep.30889. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 31378984 Free PMC article.
-
Transient intracellular expression of PD-L1 and VEGFR2 bispecific nanobody in cancer cells inspires long-term T cell activation and infiltration to combat tumor and inhibit cancer metastasis.Mol Cancer. 2025 Apr 19;24(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02253-6. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40253320 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Sunitinib and PD-L1 Blockade Enhances Anticancer Efficacy of TLR7/8 Agonist-Based Nanovaccine.Mol Pharm. 2019 Mar 4;16(3):1200-1210. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b01165. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Mol Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30620878
-
The integration of immune checkpoint inhibitors with VEGF targeted agents in advanced gastric and gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: a review on the rationale and results of early phase trials.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jan 12;14(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01034-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33436042 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Monoclonal antibody immune therapy response instrument for stratification and cost-effective personalized approaches in 3PM-guided pan cancer management.EPMA J. 2025 Mar 22;16(2):465-503. doi: 10.1007/s13167-025-00403-w. eCollection 2025 Jun. EPMA J. 2025. PMID: 40438490 Review.
-
Immunomic longitudinal profiling of the NeoPembrOv trial identifies drivers of immunoresistance in high-grade ovarian carcinoma.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 16;15(1):5932. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47000-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39013886 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Enhancing Colorectal Cancer Treatment Through VEGF/VEGFR Inhibitors and Immunotherapy.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025 Mar;26(3):213-225. doi: 10.1007/s11864-025-01306-8. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40045029 Review.
-
Characterization and functional evaluation of JS207, a novel bispecific antibody against human PD-1 and VEGFA.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1612547. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1612547. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607397 Free PMC article.
-
Co-targeting of VEGFR2 and PD-L1 promotes survival and vasculature normalization in pleural mesothelioma.Oncoimmunology. 2025 Dec;14(1):2512104. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2025.2512104. Epub 2025 May 29. Oncoimmunology. 2025. PMID: 40439143 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

