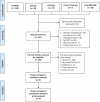
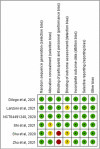
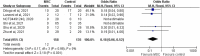The clinical efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stromal cells for patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 35849852
- PMCID: PMC9259515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.07.001
The clinical efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stromal cells for patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objectives: This meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigated the usefulness of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) to treat patients with COVID-19.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Ovid MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, and Clinicaltrials.gov were searched for RCTs published before November 7, 2021. Only RCTs that compared the clinical efficacy and safety of MSCs with other alternative treatments or placebos in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 were included.
Results: Six RCTs were included, in which the MSC and control groups consisted of 158 and 135 patients, respectively. The patients who received MSCs had a significantly lower 28-day mortality rate (7.6% vs 21.5%; OR, 0.18; 95% CI, 0.06-0.52; I2 = 0%) and significantly higher clinical improvement rate (OR, 6.05; 95% CI, 2.31-15.83; I2 = 0%) than the controls. The patients who received MSCs were associated with a similar risk of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs to the control group (AEs: OR, 33; 95% CI, 0.09-1.18; I2 = 59%; serious AEs: OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.02-4.41; I2 = 53%).
Conclusions: MSC treatment may help to improve the clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19. In addition, MSC treatment appears to be a safe therapeutic option for patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mesenchymal stromal cell; Mortality; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests This paper did not receive any funding. The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants, or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of mesenchymal stromal cells to treat coronavirus disease 2019: is it too late?Cytotherapy. 2023 Mar;25(3):341-352. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2022.10.003. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Cytotherapy. 2023. PMID: 36333234 Free PMC article.
-
Research Status of the Safety and Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of COVID-19-Related Pneumonia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Stem Cells Dev. 2021 Oct 1;30(19):947-969. doi: 10.1089/scd.2021.0179. Stem Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 34416823
-
Double-blind, randomized, controlled, trial to assess the efficacy of allogenic mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome due to COVID-19 (COVID-AT): A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 6;22(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04964-1. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33407777 Free PMC article.
-
Updated Living Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Treat COVID-19: A Framework for Accelerated Synthesis of Trial Evidence for Rapid Approval-FASTER Approval.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022 Jul 20;11(7):675-687. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szac038. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35758400 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Therapy for COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(1):143-152. doi: 10.2174/1574888X16666211206145839. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 34872483
Cited by
-
Investigational Use of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Their Secretome as Add-On Therapy in Severe Respiratory Virus Infections: Challenges and Perspectives.Adv Ther. 2023 Jun;40(6):2626-2692. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02507-z. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 37069355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell therapy for COVID-19 treatment: an umbrella review.Int J Surg. 2024 Oct 1;110(10):6402-6417. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001786. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38967503 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of clinical-grade, cryopreserved menstrual blood mesenchymal stromal cells in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 30;11:1031331. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1031331. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36793446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 〈https://covid19.who.int/〉 Accessed on June 17, 2022.
-
- Berlin D.A., Gulick R.M., Martinez F.J. Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(25):2451–2460. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi R.T., Lynch J.B., Del Rio C. Mild or Moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(18):1757–1766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous