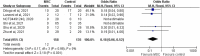The clinical efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stromal cells for patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 35849852
- PMCID: PMC9259515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.07.001
The clinical efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stromal cells for patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objectives: This meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigated the usefulness of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) to treat patients with COVID-19.
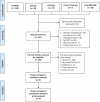
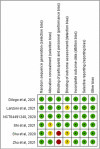
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Ovid MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, and Clinicaltrials.gov were searched for RCTs published before November 7, 2021. Only RCTs that compared the clinical efficacy and safety of MSCs with other alternative treatments or placebos in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 were included.
Results: Six RCTs were included, in which the MSC and control groups consisted of 158 and 135 patients, respectively. The patients who received MSCs had a significantly lower 28-day mortality rate (7.6% vs 21.5%; OR, 0.18; 95% CI, 0.06-0.52; I2 = 0%) and significantly higher clinical improvement rate (OR, 6.05; 95% CI, 2.31-15.83; I2 = 0%) than the controls. The patients who received MSCs were associated with a similar risk of adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs to the control group (AEs: OR, 33; 95% CI, 0.09-1.18; I2 = 59%; serious AEs: OR, 0.30; 95% CI, 0.02-4.41; I2 = 53%).
Conclusions: MSC treatment may help to improve the clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19. In addition, MSC treatment appears to be a safe therapeutic option for patients with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mesenchymal stromal cell; Mortality; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests This paper did not receive any funding. The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants, or patents received or pending, or royalties.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. 〈https://covid19.who.int/〉 Accessed on June 17, 2022.
-
- Berlin D.A., Gulick R.M., Martinez F.J. Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(25):2451–2460. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi R.T., Lynch J.B., Del Rio C. Mild or Moderate Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(18):1757–1766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous