Offset-decoupled deformable convolution for efficient crowd counting
- PMID: 35851829
- PMCID: PMC9293988
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16415-9
Offset-decoupled deformable convolution for efficient crowd counting
Abstract
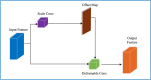
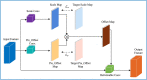
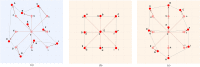
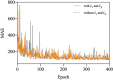
Crowd counting is considered a challenging issue in computer vision. One of the most critical challenges in crowd counting is considering the impact of scale variations. Compared with other methods, better performance is achieved with CNN-based methods. However, given the limit of fixed geometric structures, the head-scale features are not completely obtained. Deformable convolution with additional offsets is widely used in the fields of image classification and pattern recognition, as it can successfully exploit the potential of spatial information. However, owing to the randomly generated parameters of offsets in network initialization, the sampling points of the deformable convolution are disorderly stacked, weakening the effectiveness of feature extraction. To handle the invalid learning of offsets and the inefficient utilization of deformable convolution, an offset-decoupled deformable convolution (ODConv) is proposed in this paper. It can completely obtain information within the effective region of sampling points, leading to better performance. In extensive experiments, average MAE of 62.3, 8.3, 91.9, and 159.3 are achieved using our method on the ShanghaiTech A, ShanghaiTech B, UCF-QNRF, and UCF_CC_50 datasets, respectively, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods and validating the effectiveness of the proposed ODConv.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Q. Wang, J. Gao & W. Lin. NWPU-crowd: A large-scale benchmark for crowd counting and localization. in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 3013269 (2020). - PubMed
-
- V. A. Sindagi & V. M. Patel. Generating high-quality crowd density maps using contextual pyramid cnns. in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 1879–1888 (2017).
-
- Feris RS, Siddiquie B, Petterson J. Large-scale vehicle detection, indexing & search in urban surveillance videos. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2012;14(1):28–42. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2011.2170666. - DOI
-
- Wang G, Li B, Zhang Y, Yang J. Background modeling and referencing for moving cameras-captured surveillance video coding in hevc. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2018;20(11):2921–2934. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2829163. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

