Could Repeated Cardio-Renal Injury Trigger Late Cardiovascular Sequelae in Extreme Endurance Athletes?
- PMID: 35851948
- PMCID: PMC9691495
- DOI: 10.1007/s40279-022-01734-8
Could Repeated Cardio-Renal Injury Trigger Late Cardiovascular Sequelae in Extreme Endurance Athletes?
Abstract
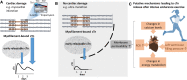
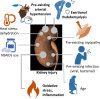
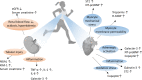
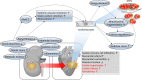
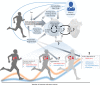
Regular exercise confers multifaceted and well-established health benefits. Yet, transient and asymptomatic increases in markers of cardio-renal injury are commonly observed in ultra-endurance athletes during and after competition. This has raised concerns that chronic recurring insults could cause long-term cardiac and/or renal damage. Indeed, extreme endurance exercise (EEE) over decades has sometimes been linked with untoward cardiac effects, but a causal relation with acute injury markers has not yet been established. Here, we summarize the current knowledge on markers of cardiac and/or renal injury in EEE athletes, outline the possible interplay between cardiac and kidney damage, and explore the roles of various factors in the development of potential exercise-related cardiac damage, including underlying diseases, medication, sex, training, competition, regeneration, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation. In conclusion, despite the undisputed health benefits of regular exercise, we speculate, based on the intimate link between heart and kidney diseases, that in rare cases excessive endurance sport may induce adverse cardio-renal interactions that under specific, hitherto undefined conditions could result in persistent cardiac damage. We highlight future research priorities and provide decision support for athletes and clinical consultants who are seeking safe strategies for participation in EEE training and competition.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
James Keefe is a participant in the Speaker Bureau for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Janssen and Lilly. He is also Chief Medical Officer and Founder of CardioTabs, a nutraceutical company, and has a major ownership interest in that company. Hans-Georg Predel holds a leadership position in the German Hypertension Society. Johannes Burtscher, Paul-Emmanuel Vanderriele, Matthieu Legrand, Josef Niebauer, Grégoire Millet and Martin Burtscher declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this review.
Figures
References
-
- Wen CP, Wai JPM, Tsai MK, Yang YC, Cheng TYD, Lee M-C, et al. Minimum amount of physical activity for reduced mortality and extended life expectancy: a prospective cohort study. The lancet. 2011;378(9798):1244–1253. - PubMed
-
- Whyte G, Sheppard M, George K, Shave R, Wilson M, Prasad S, et al. Post-mortem evidence of idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy and idiopathic interstitial myocardial fibrosis: is exercise the cause? Br J Sports Med. 2008;42(4):304–305. - PubMed

