LIPID transfer proteins regulate store-operated calcium entry via control of plasma membrane phosphoinositides
- PMID: 35853265
- PMCID: PMC9444960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2022.102631
LIPID transfer proteins regulate store-operated calcium entry via control of plasma membrane phosphoinositides
Abstract
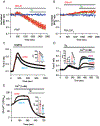
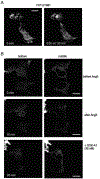
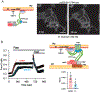
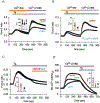
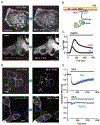
The ER-resident proteins STIM1 together with the plasma membrane (PM)-localized Orai1 channels constitute the molecular components of the store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) pathway. Prepositioning of STIM1 to the peripheral ER close to the PM ensures its efficient interaction with Orai1 upon a decrease in the ER luminal Ca2+ concentration. The C-terminal polybasic domain of STIM1 has been identified as mediating the interaction with PM phosphoinositides and hence positions the molecule to ER-PM contact sites. Here we show that STIM1 requires PM phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P) for efficient PM interaction. Accordingly, oxysterol binding protein related proteins (ORPs) that work at ER-PM junctions and consume PI4P gradients exert important control over the Ca2+ entry process. These studies reveal an important connection between non-vesicular lipid transport at ER-PM contact sites and regulation of ER Ca2+store refilling.
Keywords: Calcium; ER; Lipid transfer proteins; Membrane contact sites; Phosphatidylinositol; Phosphoinositides; Plasma membrane.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest pertinent to this study.
Figures

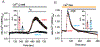
Similar articles
-
The SOAR of STIM1 interacts with plasma membrane lipids to form ER-PM contact sites.Cell Rep. 2023 Mar 28;42(3):112238. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112238. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36906853
-
Role of phosphoinositides in STIM1 dynamics and store-operated calcium entry.Biochem J. 2009 Dec 14;425(1):159-68. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090884. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19843011 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of ER-PM Junctions: A Critical Determinant in the Regulation of SOCE and TRPC1.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;981:253-276. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55858-5_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29594865
-
Tuning store-operated calcium entry to modulate Ca2+-dependent physiological processes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Jul;1866(7):1037-1045. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30521873 Review.
-
STIM1 and lipid interactions at ER-PM contact sites.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Jan 1;328(1):C107-C114. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00634.2024. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39620863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PtdSer as a signaling lipid determined by privileged localization of ORP5 and ORP8 at ER/PM junctional foci to determine PM and ER PtdSer/PI(4)P ratio and cell function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 29;120(35):e2301410120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2301410120. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37607230 Free PMC article.
-
Non-vesicular phosphatidylinositol transfer plays critical roles in defining organelle lipid composition.EMBO J. 2024 May;43(10):2035-2061. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00096-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 38627600 Free PMC article.
-
The tether function of the anoctamins.Cell Calcium. 2024 Jul;121:102875. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2024.102875. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Cell Calcium. 2024. PMID: 38701708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A molecular systems perspective on calcium oscillations beyond ion fluxes.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2025 Jun;94:102523. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2025.102523. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40311263 Review.
-
Gasdermin D deficiency aborts myeloid calcium influx to drive granulopoiesis in lupus nephritis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jun 3;22(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01681-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38831451 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

