Neurodevelopmental outcome of Italian preterm ELBW infants: an eleven years single center cohort
- PMID: 35854369
- PMCID: PMC9297614
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-022-01303-9
Neurodevelopmental outcome of Italian preterm ELBW infants: an eleven years single center cohort
Abstract
Background: Preterm extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWi) are known to be at greater risk of developing neuropsychiatric diseases. Identifying early predictors of outcome is essential to refer patients for early intervention. Few studies have investigated neurodevelopmental outcomes in Italian ELBWi. This study aims to describe neurodevelopmental outcome at 24 months of corrected age in an eleven-year single-center cohort of Italian ELBWi and to identify early risk factors for adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes.
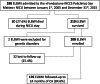
Methods: All infants born with birth weight < 1000 g and admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of the "Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo" hospital in Pavia, Italy, from Jan 1, 2005 to Dec 31, 2015 were eligible for inclusion. At 24 months, Griffiths' Mental Developmental Scales Extended Revised (GMDS-ER) were administered. Neurodevelopmental outcome was classified as: normal, minor sequelae (minor neurological signs, General Quotient between 76 and 87), major sequelae (cerebral palsy; General Quotient ≤ 75; severe sensory impairment). Univariate and multivariate multinomial logistic regression models were performed to analyze the correlation between neonatal variables and neurodevelopmental outcome.
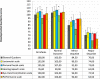
Results: 176 ELBWi were enrolled (mean gestational age 26.52 weeks sd2.23; mean birthweight 777.45 g sd142.89). 67% showed a normal outcome at 24 months, 17% minor sequelae and 16% major sequelae (4.6% cerebral palsy on overall sample). The most frequent major sequela was cognitive impairment (8.52%). In the entire sample the median score on the Hearing-Speech subscale was lower than the median scores recorded on the other subscales and showed a significantly weaker correlation to each of the other subscales of the GMDS-ER. Severely abnormal cUS findings (RRR 10.22 p 0.043) and bronchopulmonary dysplasia (RRR 4.36 p 0.008) were independent risk factors for major sequelae and bronchopulmonary dysplasia for minor sequelae (RRR 3.00 p 0.018) on multivariate multinomial logistic regression.
Conclusions: This study showed an improvement in ELBWI survival rate without neurodevelopmental impairment at 24 months compared to previously reported international cohorts. Cognitive impairment was the most frequent major sequela. Median scores on GMDS-ER showed a peculiar developmental profile characterized by a selective deficit in the language domain. Severely abnormal cUS findings and bronchopulmonary dysplasia were confirmed as independent risk factors for major sequelae.
Keywords: ELBWI; NICU; Neurodevelopment; Perinatal complications; Prematurity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurodevelopmental outcome of preterm very low birth weight infants admitted to an Italian tertiary center over an 11-year period.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 11;11(1):16316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95864-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34381139 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopmental Outcome and Neuroimaging of Very Low Birth Weight Infants from an Italian NICU Adopting the Family-Centered Care Model.Children (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;11(1):12. doi: 10.3390/children11010012. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275433 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprem: the Neuro-developmental outcome of very low birth weight infants in an Italian region.Ital J Pediatr. 2020 Feb 22;46(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0787-7. Ital J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32087748 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation or instillation of steroids for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Neonatology. 2015;107(4):358-9. doi: 10.1159/000381132. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Neonatology. 2015. PMID: 26044104 Review.
-
Extreme prematurity: Risk and resiliency.Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2022 Feb;52(2):101132. doi: 10.1016/j.cppeds.2022.101132. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2022. PMID: 35181232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In-hospital growth and long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants.Front Pediatr. 2023 May 11;11:1180068. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1180068. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37252047 Free PMC article.
-
Global inequities in the survival of extremely preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Jul 30;25(1):579. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05933-w. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40739629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Twilhaar ES, Wade RM, De Kieviet JF, Van Goudoever JB, Van Elburg RM, Oosterlaan J. Cognitive outcomes of children born extremely or very preterm since the 1990s and associated risk factors: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. JAMA Pediatr. 2018;172(4):361–367. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.5323. - DOI - PMC - PubMed