Cell osteogenic bioactivity mediated precisely by varying scaled micro-pits on ordered micro/nano hierarchical structures of titanium
- PMID: 35855110
- PMCID: PMC9290875
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbac046
Cell osteogenic bioactivity mediated precisely by varying scaled micro-pits on ordered micro/nano hierarchical structures of titanium
Abstract
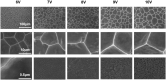
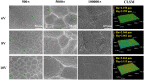
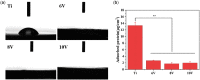
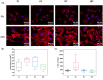
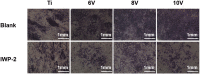
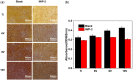
Hierarchical surface structures with micro-nano scale play a crucial role in regulation of cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. It has been proven that cells are extremely sensitive to the nanoscaled structure and show multifarious phenotypes. Though a vital function of microstructure on osseointegration has been confirmed, the cell performances response to different microscaled structure is needed to be further dissected and in depth understood. In this work, the ordered micro-nano hierarchical structures with varying micro-scaled pits were precisely fabricated on titanium successfully by the combination of electrochemical, chemical etching and anodization as well. In vitro systematical assessments indicated that the micro-nano multilevel structures on titanium exhibited excellent cells adhesion and spreading ability, as well as steerable proliferation and osteogenic differentiation behaviors. It is shown that smaller micro-pits and lower roughness of the hierarchical structures enabled faster cell propagation. Despite cell growth was delayed on micro-nano titanium with relatively larger cell-match-size micro-pits and roughness, osteogenic-specific genes were significantly elevated. Furthermore, the alkaline phosphatase activity, collagen secretion and extracellular matrix mineralization of MC3T3-E1 on multi-scaled titanium were suppressed by a large margin after adding IWP-2 (an inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway), indicating this pathway played a crucial part in cell osteogenic differentiation modulated by micro-nano structures.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin; electrochemical self-organizing etching; osteogenic; varying micro-scaled pits.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures









References
-
- Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK.. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—a review. Prog Mater Sci 2009;54:397–425.
-
- Niinomi M. Biologically and mechanically biocompatible titanium alloys. Mater Trans 2008;49:2170–8.
-
- Yoon IK, Hwang JY, Jang W-C, Kim HW, Shin US.. Natural bone-like biomimetic surface modification of titanium. Appl Surf Sci 2014;301:401–9.
-
- Terleeva OP, Sharkeev YP, Slonova AI, Mironov IV, Legostaeva EV, Khlusov IA, Matykina E, Skeldon P, Thompson GE.. Effect of microplasma modes and electrolyte composition on micro-arc oxidation coatings on titanium for medical applications. Surf Coat Technol 2010;205:1723–9.
-
- Cheng MQ, Qiao YQ, Wang Q, Jin GD, Qin H, Zhao YC, Peng XC, Zhang XL, Liu XY.. Calcium plasma implanted titanium surface with hierarchical microstructure for improving the bone formation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015;7:13053–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

