Treatment of transient prosopagnosia with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor in a case of brain metastasis from EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35855154
- PMCID: PMC9282735
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_500_2022
Treatment of transient prosopagnosia with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor in a case of brain metastasis from EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Prosopagnosia is a rare form of apraxia, in which a person has normal memory and vision, but has impaired cognition of human faces that are manifested through symptoms such as not being able to recognize the face of a familiar person, one has known or not being able to remember the face of a person. Here, we report the case of a patient with transient prosopagnosia associated with brain metastasis from epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma who was treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
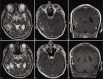
Case description: A 52-year-old right-handed man with lung adenocarcinoma was introduced to our department because brain metastasis. On admission, he complained that he could not recognize his wife's face, but he could recall her face based on her voice. MRI revealed a right temporo-occipital enhancing lesion with perifocal edema and dissemination that were indicative of brain metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma. Two weeks after open biopsy, he was started on TKI therapy with osimertinib at a dosage of 80 mg/day. An MRI scan taken 1 month later revealed shrinkage of the metastasis. In addition, he had recovered from transient prosopagnosia and returned to normal life.
Conclusion: In this study, the TKI osimertinib was administered to a patient with brain metastasis of EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma who presented with prosopagnosia, and the patient's lesion shrunk and his symptoms were reversed with this treatment.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; Lung adenocarcinoma; Prosopagnosia; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Transient prosopagnosia after removal of a tumor in the right occipito-temporal cortex: a case report].No Shinkei Geka. 2008 Nov;36(11):1023-7. No Shinkei Geka. 2008. PMID: 19048922 Japanese.
-
Treating Choroidal Metastases and Improving Vision with Osimertinib in EGFR T790M-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Ocul Oncol Pathol. 2021 Mar;7(1):26-30. doi: 10.1159/000510602. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Ocul Oncol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33796513 Free PMC article.
-
Right Fusiform Gyrus Infarct with Acute Prosopagnosia.Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2022 Dec 30;31(4):186-187. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2022. PMID: 35470413
-
Outcome of EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma NSCLC patients with changed phenotype to squamous cell carcinoma after tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A pooled analysis with an additional case.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jan;127:12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.11.016. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30642539 Review.
-
Osimertinib: A third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer with the acquired Thr790Met mutation.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018 Jul;24(5):379-388. doi: 10.1177/1078155217712401. Epub 2017 May 31. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018. PMID: 28565936 Review.
References
-
- Anderson CA, Woodcock JH, Filley CM. Transient prosopagnosia with right temporal astrocytoma. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;28:e13–4. - PubMed
-
- Corrivetti F, Herbet G, Moritz-Gasser S, Duffau H. Prosopagnosia induced by a left anterior temporal lobectomy following a right temporo-occipital resection in a multicentric diffuse low-grade glioma. World Neurosurg. 2017;97:756.e1–5. - PubMed
-
- Genova HM, Rajagopalan V, Chiaravalloti N, Binder A, Deluca J, Lengenfelder J. Facial affect recognition linked to damage in specific white matter tracts in traumatic brain injury. Soc Neurosci. 2015;10:27–34. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
