Incidence of radiographic scoliosis in asymptomatic young Pakistani adults
- PMID: 35855158
- PMCID: PMC9282810
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_1230_2021
Incidence of radiographic scoliosis in asymptomatic young Pakistani adults
Abstract
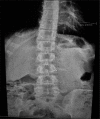
Background: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is the most common scoliotic deformity of young adults. Screening of AIS is performed as part of the routine preemployment examination for physically demanding positions. We attempted to establish the incidence of clinically overt scoliosis in an adolescent (16 years old) and young adult (21 years old) population.
Methods: We clinically and radiographically (X-rays) evaluated 85 applicants for physically demanding jobs in two age groups: those 16 versus those 21 years of age. Cobb's angles and kyphosis angles were measured for each group. These data were then categorized into three grades based on radiographically documented scoliotic curvatures.
Results: Most 16 years old demonstrated normal Cobb's angles (90.56%), but kyphosis angles of 20-30° (40.27%). For the 21 years old, most participants had normal Cobb's angles (93.75%), but exhibited higher than normal kyphosis angles (50%).
Conclusion: Most young adults ages 16-21 years applying for physically demanding work were "fit." However, the incidence of kyphosis was higher among the 21 years old population. Such screening for idiopathic scoliosis should be more stringently performed in younger patients applying for physically demanding work.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Scoliosis; Spine; X-ray.
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel evaluation index for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis progression measurement and diagnosis.Technol Health Care. 2014 Jan 1;22(2):225-41. doi: 10.3233/THC-140779. Technol Health Care. 2014. PMID: 24561884
-
Curve severity and apical vertebral rotation and their association with curve flexibility in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Musculoskelet Surg. 2021 Dec;105(3):303-308. doi: 10.1007/s12306-020-00660-0. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Musculoskelet Surg. 2021. PMID: 32323201 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the sagittal profiles among thoracic idiopathic scoliosis patients with different Cobb angles and growth potentials.J Orthop Surg Res. 2014 Mar 17;9:19. doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-9-19. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014. Retraction in: J Orthop Surg Res. 2015 Mar 26;10:44. doi: 10.1186/s13018-015-0181-0. PMID: 24635839 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Association of spinal deformity and pelvic tilt with gait asymmetry in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients: Investigation of ground reaction force.Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2016 Jul;36:52-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 13. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2016. PMID: 27214246
-
Preoperative Sagittal Spinal Profile of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Lenke Types and Non-Scoliotic Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019 Jan 15;44(2):134-142. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002748. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019. PMID: 29927859
References
-
- Dunn J, Henrikson NB, Morrison CC, Nguyen M, Blasi PR, Lin JS. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018. Jan, Screening for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Evidence Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Report No.: 17-05230EF-1. - PubMed
-
- Fong DY, Cheung KM, Wong YW, Wan YY, Lee CF, Lam TP, et al. A population-based cohort study of 394,401 children followed for 10 years exhibits sustained effectiveness of scoliosis screening. Spine J. 2015;15:825–33. - PubMed
-
- Hengwei F, Zifang H, Qifei W, Weiqing T, Nali D, Ping Y, et al. Prevalence of idiopathic scoliosis in Chinese schoolchildren: A large, population-based study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41:259–64. - PubMed
-
- Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, Bridwell KH, Clements DH, Lowe TG, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A new classification to determine extent of spinal arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83:1169–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources