Temporary standalone percutaneous fixation with pedicle screws for the treatment of subacute tuberculous osteomyelitis with kyphotic deformity in the lumbar spine
- PMID: 35855170
- PMCID: PMC9282791
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_457_2022
Temporary standalone percutaneous fixation with pedicle screws for the treatment of subacute tuberculous osteomyelitis with kyphotic deformity in the lumbar spine
Abstract
Background: Tuberculous (TB) osteomyelitis is a rare, but challenging infection, that mandates antituberculosis antibiotics, and potentially surgical intervention. Per the Gulhane Askeri Tip Akademisi (GATA) classification system, corrective reconstruction is indicated in severe cases, where the kyphotic deformity is >20° (GATA Class III). Here, we describe a case of BCG vaccine-induced lumbar TB osteomyelitis at the L1-2 level in a patient presenting with mechanical pain and a focal, nonfixed kyphotic deformity of 36.1°. Surgery consisted of percutaneous fixation with pedicle screws without debridement, fusion arthrodesis, or anterior reconstruction.
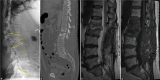
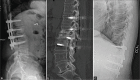
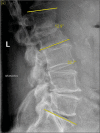
Case description: A 77-year-old male presented with L1-2 TB osteomyelitis secondary to intravesical BCG application. A 36.1° focal nonfixed kyphotic deformity was evident on standing X-rays that reduced in the supine position. He underwent posterior percutaneous screw fixation with rods extending from the T12 to L3 levels, with resolution of his mechanical pain. Nine months later, the CT demonstrated reconstitution of the vertebral bodies (i.e., volume increase of 6.99 cm3 (21%) and 7.49 cm3 (27%) at L1 and L2, respectively). Standing X-rays after hardware removal demonstrated 32.7° of lumbar lordosis and a reduction of focal kyphosis to 12.9°.
Conclusion: Here, we present an exceedingly rare case of BCG vaccine-induced L1-2 spinal tuberculosis with extensive vertebral body destruction and deformity. This was effectively treated with standalone temporary pedicle fixation instead of corpectomy and reconstruction.
Keywords: BCG vaccine; GATA classification; Percutaneous fixation; Spinal tuberculosis; Tuberculous osteomyelitis.
Copyright: © 2022 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Broekx S, Buelens E. Tuberculous spondylitis following intravesical bcg-instillation in the treatment of transitional cell carcinoma: Case report and systematic review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;194:105944. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho B, Pereira P, Silva PS, Silva J, Pinto M, Vazs R. Lumbar tuberculous spondylodiscitis: A minimally invasive surgical approach. Acta Reumatol Port. 2011;36:57–60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
