Surgical management for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease by a transcranial biopsy combined with extraorbital decompression: illustrative case
- PMID: 35855308
- PMCID: PMC9241348
- DOI: 10.3171/CASE20170
Surgical management for IgG4-related ophthalmic disease by a transcranial biopsy combined with extraorbital decompression: illustrative case
Abstract
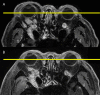
Background: Immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease (IgG4-ROD) accounts for 22% of Japanese lymphoproliferative orbital disease and occurs in 4%-34% of patients with IgG4-related disease, according to the largest case series published to date. Because the optic nerve mass often appears as a tumor-like lesion, it is important, although difficult, to differentiate IgG4-ROD from other orbital tumors and diseases, and biopsy is essential for diagnosis. Here, the authors describe the surgical management of an IgG4-ROD case.
Observations: A 63-year-old man presented to the authors' hospital with proptosis and visual impairment. Ophthalmic examination revealed intraocular hypertension. IgG4-related disease with an ophthalmic lesion was suspected on the basis of a blood test and imaging studies. Transcranial biopsy with extraorbital decompression was performed. The patient's symptoms, including visual impairment, improved 3 days after operation, and his IgG4-related disease resolved after corticosteroid treatment.
Lessons: The standard treatment for IgG4-related disease is systemic corticosteroid therapy. However, this treatment should not be administered to patients with IgG4-ROD who a high risk of blindness. In this case, the authors completed a diagnostic and symptom-relieving transcranial biopsy without affecting the patient's aesthetic characteristics. This is the first study, to our knowledge, to report extraorbital decompression via a transcranial approach as a surgical option for IgG4-ROD.
Keywords: FT = frontotemporal; IgG4-ROD = immunoglobulin G4–related ophthalmic disease; IgG4-related disease; IgG4-related ophthalmic diseases; LogMAR = logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution; MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; extraorbital decompression; orbital tumor; transcranial orbital approach.
© 2021 The authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Japanese study group of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease. A prevalence study of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease in Japan. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2013;57(6):573–579. - PubMed
-
- Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, et al. Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(8):1310–1315. - PubMed
-
- Noshiro S, Wanibuchi M, Akiyama Y, et al. IgG4-related disease initially presented as an orbital mass lesion mimicking optic nerve sheath meningioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2015;32(4):286–290. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

