The Effects of Virtual Directed Painting Therapy on Anxiety, Depression, and Self-efficacy of Children with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35855382
- PMCID: PMC9287569
- DOI: 10.30476/IJCBNM.2022.93400.1927
The Effects of Virtual Directed Painting Therapy on Anxiety, Depression, and Self-efficacy of Children with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Diabetes-induced anxiety, depression, and decreased self-efficacy lead to poor adherence to treatment in diabetic children. Since painting therapy seems to be helpful to express their feelings, this study aimed to investigate the effects of virtual directed painting therapy on anxiety, depression, and self-efficacy in diabetic children.
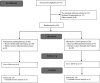
Methods: This randomized controlled trial was conducted on 40 children with type 1 diabetes aged 8-12 years who were referred to Imam Reza Clinic of Diabetes in Shiraz, from July to October 2020. Children were randomly selected and assigned to intervention and control groups, using block randomization. The intervention group received the routine care plus virtual painting therapy directed by WhatsApp (six 2-hour group sessions once a week for six weeks). Spence Children's Anxiety Scale, Maria Kovacs Children's Depression Inventory, and Diabetes Management Self-Efficacy Scale were completed before and after the intervention. Data were analyzed through SPSS 23, using Chi-square, Mann-Whitney U, and Wilcoxon tests. P value <0.05 was considered as significant.
Results: After the intervention, the median (interquartile range) total scores for anxiety, depression, and self-efficacy in the intervention group were 48.50 (45.00-51.75), 7.00 (4.00-9.00), and 169.00 (154.00-178.00), and in the control group 55.00 (48.50-62.25), 13.00 (10.00-17.50), and 152.00, respectively (110.50-184.00). After the intervention, there was a significant difference between the groups regarding anxiety (P=0.02) and depression (P<0.001); however, the difference in self-efficacy was not significant (P=0.20).
Conclusion: Painting therapy should be considered as a part of care programs in diabetes centers and other community settings to control anxiety and depression of diabetic children.
Trial registration number: IRCT20200118046181N1.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Self-efficacy; Type 1 diabetes; Virtual directed paintings therapy.
Copyright: © International Journal of Community Based Nursing and Midwifery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Coping Skills Training on Depression, Anxiety, Stress, and Self-Efficacy in Adolescents with Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2018 Oct;6(4):324-333. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2018. PMID: 30465005 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Painting on Depression in Children with Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2017 Mar-Apr;22(2):102-105. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.IJNMR_242_15. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2017. PMID: 28584546 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Filial Therapy on Depressive Symptoms of Children with Cancer and Their Mother's Depression, Anxiety, and Stress: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019 Oct 1;20(10):2935-2941. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.10.2935. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019. PMID: 31653138 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Parental Stress, Anxiety and Depression Symptoms Associated with Self-Efficacy in Paediatric Type 1 Diabetes: A Literature Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 28;18(1):152. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010152. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33379307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychological interventions to improve self-management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(28):1-232. doi: 10.3310/hta24280. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32568666 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of therapeutic artistic activities on anxiety and psychological well-being in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled study.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Jun 3;184(7):386. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06237-y. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40461873 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of yoga therapy directed by virtual training on depression of adolescent girls with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Jul 1;22(2):1273-1281. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01245-x. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 37975133 Free PMC article.
-
Hotspots, trends, and advice: a 10-year visualization-based analysis of painting therapy from a scientometric perspective.Front Psychol. 2023 May 22;14:1148391. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1148391. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37284478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of art therapy interventions on anxiety in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Jun 26;79:100404. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100404. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 38936289 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the art therapy interventions to alleviate depression symptoms among children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025 May 13;80:100683. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100683. eCollection 2025. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40367574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogle GD, von Oettingen JE, Middlehurst AC, et al. Levels of type 1 diabetes care in children and adolescents for countries at varying resource levels. Pediatric Diabetes. 2019;20:93–8. - PubMed
-
- Aminzadeh M, Navidi N, Valavi E, Aletayeb SMH. Childhood onset type 1 diabetes at a tertiary hospital in south-western Iran during 2000-2015: Rapid increase in admissions and high prevalence of DKA at diagnosis. Primary Care Diabetes. 2019;13:43–8. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen LA, Pouwer F, Lodder P, et al. Depression and anxiety in adolescents with type 1 diabetes and their parents. Pediatric Research. 2022;91:188–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical