Cognitive Dimensions of Learning in Children With Problems in Attention, Learning, and Memory
- PMID: 35855686
- PMCID: PMC7613068
- DOI: 10.1037/edu0000644
Cognitive Dimensions of Learning in Children With Problems in Attention, Learning, and Memory
Abstract
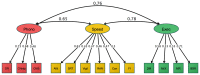
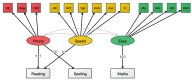
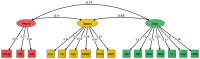
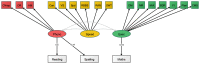
A data-driven, transdiagnostic approach was used to identify the cognitive dimensions linked with learning in a mixed group of 805 children aged 5 to 18 years recognised as having problems in attention, learning and memory by a health or education practitioner. Assessments included phonological processing, information processing speed, short-term and working memory, and executive functions, and attainments in word reading, spelling, and maths. Data reduction methods identified three dimensions of phonological processing, processing speed and executive function for the sample as a whole. This model was comparable for children with and without ADHD. The severity of learning difficulties in literacy was linked with phonological processing skills, and in maths with executive control. Associations between cognition and learning were similar across younger and older children and individuals with and without ADHD, although stronger links between learning-related problems and both executive skills and processing speed were observed in children with ADHD. The results establish clear domain-specific cognitive pathways to learning that distinguish individuals in the heterogeneous population of children struggling to learn.
Keywords: ADHD; cognition; learning difficulties; maths; reading; transdiagnostic.
Figures
References
-
- Alloway T. Automated Working Memory Assessment (AWMA) Pearson Assessment; 2007.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed American Psychiatric Pub; 2013.
-
- Araújo S, Reis A, Petersson KM, Faísca L. Rapid automatized naming and reading performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology. 2015;107(3):868–883. doi: 10.1037/edu0000006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
