Recent Progress in the Development of Opaganib for the Treatment of Covid-19
- PMID: 35855741
- PMCID: PMC9288228
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S367612
Recent Progress in the Development of Opaganib for the Treatment of Covid-19
Abstract
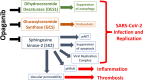
The Covid-19 pandemic driven by the SARS-CoV-2 virus continues to exert extensive humanitarian and economic stress across the world. Although antivirals active against mild disease have been identified recently, new drugs to treat moderate and severe Covid-19 patients are needed. Sphingolipids regulate key pathologic processes, including viral proliferation and pathologic host inflammation. Opaganib (aka ABC294640) is a first-in-class clinical drug targeting sphingolipid metabolism for the treatment of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Recent work demonstrates that opaganib also has antiviral activity against several viruses including SARS-CoV-2. A recently completed multinational Phase 2/3 clinical trial of opaganib in patients hospitalized with Covid-19 demonstrated that opaganib can be safely administered to these patients, and more importantly, resulted in a 62% decrease in mortality in a large subpopulation of patients with moderately severe Covid-19. Furthermore, acceleration of the clearance of the virus was observed in opaganib-treated patients. Understanding the biochemical mechanism for the anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of opaganib is essential for optimizing Covid-19 treatment protocols. Opaganib inhibits three key enzymes in sphingolipid metabolism: sphingosine kinase-2 (SK2); dihydroceramide desaturase (DES1); and glucosylceramide synthase (GCS). Herein, we describe a tripartite model by which opaganib suppresses infection and replication of SARS-CoV-2 by inhibiting SK2, DES1 and GCS. The potential impact of modulation of sphingolipid signaling on multi-organ dysfunction in Covid-19 patients is also discussed.
Keywords: ABC294640; dihydroceramide desaturase; glucosylceramide synthase; opaganib; sphingolipid; sphingosine kinase.
© 2022 Smith et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Charles D. Smith, Lynn W. Maines and Staci N. Keller are current employees and own stock in Apogee Biotechnology Corporation. In addition, Dr Charles D Smith has patents (7,338,961; 8,063,248; 8,557,800) licensed to RedHill Biopharma LTD. Dr Lynn W Maines reports patents (8324237; 8685936) issued to RedHill Biopharma. Vered Katz Ben-Yair, Reza Fathi, Terry F. Plasse and Mark L. Levitt are currently paid consultants to RedHill Biopharma LTD. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

