Natural language processing: state of the art, current trends and challenges
- PMID: 35855771
- PMCID: PMC9281254
- DOI: 10.1007/s11042-022-13428-4
Natural language processing: state of the art, current trends and challenges
Abstract
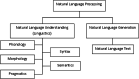
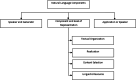
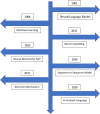
Natural language processing (NLP) has recently gained much attention for representing and analyzing human language computationally. It has spread its applications in various fields such as machine translation, email spam detection, information extraction, summarization, medical, and question answering etc. In this paper, we first distinguish four phases by discussing different levels of NLP and components of Natural Language Generation followed by presenting the history and evolution of NLP. We then discuss in detail the state of the art presenting the various applications of NLP, current trends, and challenges. Finally, we present a discussion on some available datasets, models, and evaluation metrics in NLP.
Keywords: NLP applications; NLP evaluation metrics; Natural language generation; Natural language processing; Natural language understanding.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.corrected publication 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe first draft of this paper was written under the supervision of Dr. Kiran Khatter and Dr. Sukhdev Singh, associated with CL- Educate: Accendere Knowledge Management Services Pvt. Ltd. and deputed at the Manav Rachna International University. The draft is also available on arxiv.org at https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05148
Figures
References
-
- Ahonen H, Heinonen O, Klemettinen M, Verkamo AI (1998) Applying data mining techniques for descriptive phrase extraction in digital document collections. In research and technology advances in digital libraries, 1998. ADL 98. Proceedings. IEEE international forum on (pp. 2-11). IEEE
-
- Alshawi H (1992) The core language engine. MIT press
-
- Alshemali B, Kalita J. Improving the reliability of deep neural networks in NLP: A review. Knowl-Based Syst. 2020;191:105210. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105210. - DOI
-
- Andreev ND. The intermediary language as the focal point of machine translation. In: Booth AD, editor. Machine translation. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company; 1967. pp. 3–27.
-
- Androutsopoulos I, Paliouras G, Karkaletsis V, Sakkis G, Spyropoulos CD, Stamatopoulos P (2000) Learning to filter spam e-mail: A comparison of a naive bayesian and a memory-based approach. arXiv preprint cs/0009009
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources