Reveal the Mechanisms of Yi-Fei-Jian-Pi-Tang on Covid-19 through Network Pharmacology Approach
- PMID: 35855804
- PMCID: PMC9288182
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1493137
Reveal the Mechanisms of Yi-Fei-Jian-Pi-Tang on Covid-19 through Network Pharmacology Approach
Abstract
Objectives: The Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formula Yi-Fei-Jian-Pi-Tang (YFJPT) has been demonstrated effective against Corona Virus Disease 2019 (Covid-19). The aim of this article is to make a thorough inquiry about its active constituent as well as mechanisms against Covid-19 via TCM network pharmacology.
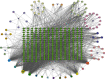
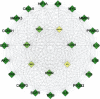
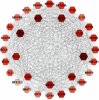
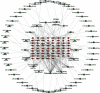
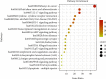
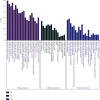
Methods: All the ingredients of YFJPT are obtained from the pharmacology database of the TCM system. The genes which are associated with the targets are obtained by utilizing UniProt. The herb-target network is built up by utilizing Cytoscape. The target protein-protein interaction network is built by utilizing the STRING database and Cytoscape. The critical targets of YFJPT are explored by Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG).
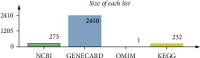
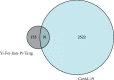
Results: The outcomes show that YFJPT might has 33 therapeutic targets on Covid-19, namely, interleukin 2 (IL2), heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1), interleukin 4 (IL4), interferon gamma (FNG), α nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in Bcells inhibitor, alpha (NFKBIA), nuclear factor-k-gene binding (NFKB), nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1), hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha (HIF1A), mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (MAPK3), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), interleukin 10 (IL10), jun proto-oncogene (JUN), C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CXCL8), tumor protein p53 (TP53), interleukin 1 beta (IL1B), AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (AKT1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin 6 (IL6), erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (ERBB2), RELA proto-oncogene (RELA), NF-κB subunit, caspase 8 (CASP8), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARA), TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 1 (TIMP1), transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFB1), interleukin 1 alpha (IL1A), signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8), myeloperoxidase (MPO), matrix metallopeptidase 3 (MMP3), matrix metallopeptidase 1 (MMP1), and NFE2 like bZIP transcription factor 2 (NFE2L2). The gene enrichment analysis prompts that YFJPT most likely contributes to patients related to Covid-19 by regulating the pathways of cancers.
Conclusions: That will lay a foundation for the clinical rational application and further experimental research of YFJPT.
Copyright © 2022 Wanying Lang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Li L., Wang Z., Wang J., Zheng Y., Li Z., Wang Q. Enlightenment about Using TCM Constitutions for Individualized Medicine and Construction of Chinese-style Precision Medicine: Research Progress with TCM Constitutions. Science China. Life sciences . 2020;64(12):2092–2099. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1872-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

