BMSC-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating AKT/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy of Nucleus Pulposus Cells
- PMID: 35855812
- PMCID: PMC9288351
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9896444
BMSC-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Modulating AKT/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy of Nucleus Pulposus Cells
Abstract
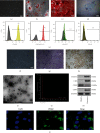
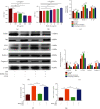
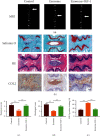
The pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is still unclear. It has been shown that the pathological process of IDD is most closely related to inflammation of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs), in which inflammatory factors play an important role. Exosomes are the main paracrine mediators and are microvesicles with biological functions similar to those of the cells from which they are derived. Studies have shown that bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) can inhibit apoptosis of NPCs by sending exosomes as anti-inflammatory and antioxidant, which has been proved to be effective on IDD. However, the specific mechanism of inhibiting apoptosis of NPCs is still unclear. In our study, BMSC-derived exosomes (BMSC-Exo) were isolated from the BMSC culture medium, and their antiapoptotic effects were evaluated in cells and rat models to explore the possible mechanisms. We observed that BMSC-Exo promotes autophagy in NPCs and inhibits the release of inflammatory factors such as IL-1β and TNF-α in LPS-treated NPCs and inhibits apoptosis in NPCs. Further studies showed that BMSC-Exo inhibited the Akt-mTOR pathway. Intramuscular injection of BMSC-Exo alleviates disc degeneration in rat IDD models. In conclusion, our results suggest that BMSC-Exo can reduce NPC apoptosis and alleviate IDD by promoting autophagy by inhibiting the Akt-mTOR pathway. Our study confers a promising therapeutic strategy for IDD.
Copyright © 2022 Quan Xiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bone mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous lncRNA CAHM via exosomes to regulate macrophage polarization and ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration.Exp Cell Res. 2022 Dec 15;421(2):113408. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113408. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Exp Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 36334792
-
Therapeutic effect of co-culture of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and degenerated nucleus pulposus cells on intervertebral disc degeneration.Spine J. 2021 Sep;21(9):1567-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.05.007. Epub 2021 May 14. Spine J. 2021. PMID: 34000376
-
circ_0072464 Shuttled by Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secreted Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis to Relieve Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 29;2022:2948090. doi: 10.1155/2022/2948090. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35814268 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells and their exosomes application in the treatment of intervertebral disc disease: A promising frontier.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Apr;105:108537. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108537. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35101851 Review.
-
The role of IL-1β and TNF-α in intervertebral disc degeneration.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110660. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110660. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32853910 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural products can modulate inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1150835. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1150835. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36874009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal Noncoding RNAs as Alternative Treatments for Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Current Status and Future Perspectives.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2023 Oct;16(5):1085-1098. doi: 10.1007/s12265-023-10401-w. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37286924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends and emerging frontiers of mesenchymal stem cells in intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric analysis (2000-2024).Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 25;12:1601806. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1601806. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40636356 Free PMC article.
-
Heme oxygenase 1‑overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell‑derived exosomes suppress interleukin‑1 beta‑induced apoptosis and aging of nucleus pulposus cells.Mol Med Rep. 2025 May;31(5):116. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13481. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40052562 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in skeletal diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jun 6;11:1268019. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1268019. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38903180 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

