Investigating the Mechanisms of Jieduquyuziyin Prescription Improves Lupus Nephritis and Fibrosis via FXR in MRL/lpr Mice
- PMID: 35855861
- PMCID: PMC9288302
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4301033
Investigating the Mechanisms of Jieduquyuziyin Prescription Improves Lupus Nephritis and Fibrosis via FXR in MRL/lpr Mice
Abstract
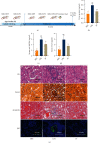
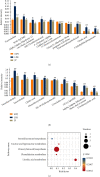
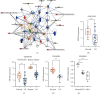
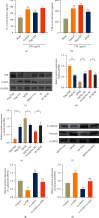
Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most serious complications of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and one of the leading causes of death. An alternative effective treatment to ameliorate and relieve LN and delay the process of renal tissue fibrosis is urgently needed in the clinical setting. Jieduquyuziyin prescription (JP) has been successfully used to treat SLE, but its potential mechanisms are not sufficiently understood. In this study, we treated MRL/lpr mice with JP for 8 weeks and treated human renal tubular epithelial cells (human kidney 2 (HK-2)) with drug-containing serum to observe the antagonistic effects of JP on inflammation and fibrosis, as well as to investigate the possible mechanisms. Results demonstrated that JP significantly reduced urinary protein and significantly improved pathological abnormalities. Metabolomics combined with ingenuity pathway analysis illustrated that the process of kidney injury in lupus mice may be closely related to farnesoid X receptor (FXR) pathway abnormalities. Microarray biomimetic analysis and LN patients indicated that FXR may play a protective role as an effective therapeutic target for LN and renal fibrosis. JP significantly increased the expression of FXR and inhibited the expression of its downstream targets, namely, nuclear transcription factor κB (NF-κB) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), in the kidney of MRL/lpr mice and HK-2 cells, as confirmed by in vitro and in vivo experiments. In conclusion, JP may mediate the activation of renal FXR expression and inhibit NF-κB and α-SMA expression to exert anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects for LN prevention and treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Jingqun Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Jieduquyuziyin prescription promotes the efficacy of prednisone via upregulating Nrf2 in MRL/lpr kidneys.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115643. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115643. Epub 2022 Aug 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36031105
-
Complement factor B inhibitor LNP023 improves lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113433. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113433. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36076550
-
Icariin alleviates murine lupus nephritis via inhibiting NF-κB activation pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome.Life Sci. 2018 Sep 1;208:26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30146016
-
Molecular and Cellular Mediators of Renal Fibrosis in Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 14;26(6):2621. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062621. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors in the Development of Lupus Nephritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:6012715. doi: 10.1155/2016/6012715. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27403037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of herbal traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of lupus nephritis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 24;13:981063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.981063. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36506523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of novel biomarkers for lupus nephritis.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Jan 14;25(2):406-424. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10450. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 38980684 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal regulation of SIRT1 and AMPK by Ginsenoside compound K impedes the conversion from plasma cells to mitigate for podocyte injury in MRL/lpr mice in a B cell-specific manner.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Mar;48(2):190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.11.006. Epub 2023 Dec 3. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 38465215 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Mechanisms of Bile Acids Targeting the Farnesoid X Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 20;25(24):13656. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413656. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769418 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the therapeutic mechanism of Jiedu-Quyu-Ziyin Fang on systemic lupus erythematosus through the ERα-miRNA-TLR7 immune axis.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 8;10(12):e32752. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32752. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38948043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fan Y. Clinical exploration and practice of traditional Chinese medicine in systemic lupus erythematosus. Zhejiang Chinese Medical University . 2019;43(10):1030–1035.
-
- Fan Y., Wen C., Li X., Wang X. National Seminar on Research Progress of Rheumatism with Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine . Kunming, Yunnan, China: China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House; 2011. Study on the Synergistic Effect of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

