The neuroprotective effect of Xylopia parviflora against aluminum chloride-induced neurotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 35855984
- PMCID: PMC9287802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09896
The neuroprotective effect of Xylopia parviflora against aluminum chloride-induced neurotoxicity in rats
Abstract
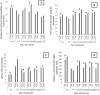
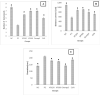
Neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer's disease, are progressive disorders which has been linked to oxidative imbalance and associated perturbations characterised by loss of memory, cognition and cholinergic deficit. To date, cholinesterase inhibition and neuroprotection are the two major strategies in drug development. Xylopia parviflora (Annonacea family) is a spice consumed in Cameroon and has been used in traditional medicine to treat various pains. In this study, X. parviflora was evaluated on behavioural studies, ion homeostasis, cholinesterase inhibitory and antioxidant activities. Rats were exposed to aluminium chloride (75 mg/kg) during 60 days, and were treated with the extract of X. parviflora (150 and 300 mg/kg BW) and two drugs references (Donepezil and Curcumin). Behavioural parameters were assessed using the Morris-Maze test and the Open Field, followed by biochemical investigations, namely, cholinesterase enzyme activity (AChE and BChE), oxidative stress (NO, MDA, GSH level, SOD and Catalase activities) and ion homeostasis (Mg2+ and Ca2+ levels). AlCl3 administration shows a decrease in learning and memory improvement during behavioural studies, significant alteration of the central cholinergic system characterised by an increase in AChE and BChE activities to 2.72 ± 0.002 mol/min/g and 5.74 ± 0.12 mol/min/g respectively, disturbance of ion homeostasis with an increase in Ca2+ level (25.68 ± 3.78 μmol/mg protein) and a decrease in Mg2+ level (15.97 ± 2.05 μmol/mg protein) and an increase in oxidative stress compared to the positive control group. Treatment with the different doses of X. parviflora increased memory and improved locomotion, improved cholinesterase activities, ion homeostasis and stabilized brain oxidative stress levels. The study suggests that X. parviflora could potentially be used for the management of some biochemical alterations associated with Alzheimer's disease. It could even be a good alternative to chemical drugs for neurotoxicity and memory enhancement.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Antioxidant stress marker; Cholinesterase; Cognitive function; Neurotoxicity; Xylopia parviflora.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- McGirr S., Venegas C., Swaminathan A. Alzheimer’s Disease: A brief review. J. Exp. Neurol. 2020;1(3):89–98.
-
- Wolters F.J., Ikram M.A. Epidemiology of vascular dementia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019;39:1542–1549. - PubMed
-
- Kriebel-Gasparro A. Update on treatments for cognitive decline in alzheimer’s disease. J. Nurse Practical. 2020;16:181–185.
-
- Kabir M.T., Bin-Jumah M.N., Uddin M.S., Bungau S.G., Zaman S., Mousa S.A., Begum Y., Ashraf G.M., Abdel-Daim M.M. Molecular mechanisms of metal toxicity in the pathogenesis of alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021;58:1–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

