Drosophila eugracilis - Akt
- PMID: 35856017
- PMCID: PMC9287739
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000544
Drosophila eugracilis - Akt
Abstract
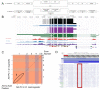
Gene Model for Akt in the D. eugracilis (DeugGB2) assembly (GCA_000236325.2).
Copyright: © 2022 by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Bock, I.R., Wheeler, M.R. (1972). The Drosophila melanogaster species group. Univ. Texas Publs Stud. Genet. 7(7213): 1--102.
-
- Chen ZX, Sturgill D, Qu J, Jiang H, Park S, Boley N, Suzuki AM, Fletcher AR, Plachetzki DC, FitzGerald PC, Artieri CG, Atallah J, Barmina O, Brown JB, Blankenburg KP, Clough E, Dasgupta A, Gubbala S, Han Y, Jayaseelan JC, Kalra D, Kim YA, Kovar CL, Lee SL, Li M, Malley JD, Malone JH, Mathew T, Mattiuzzo NR, Munidasa M, Muzny DM, Ongeri F, Perales L, Przytycka TM, Pu LL, Robinson G, Thornton RL, Saada N, Scherer SE, Smith HE, Vinson C, Warner CB, Worley KC, Wu YQ, Zou X, Cherbas P, Kellis M, Eisen MB, Piano F, Kionte K, Fitch DH, Sternberg PW, Cutter AD, Duff MO, Hoskins RA, Graveley BR, Gibbs RA, Bickel PJ, Kopp A, Carninci P, Celniker SE, Oliver B, Richards S. Comparative validation of the D. melanogaster modENCODE transcriptome annotation. Genome Res. 2014 Jul 1;24(7):1209–1223. doi: 10.1101/gr.159384.113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
