Dynamics of tumor-associated macrophages in a quantitative systems pharmacology model of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 35856032
- PMCID: PMC9287616
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104702
Dynamics of tumor-associated macrophages in a quantitative systems pharmacology model of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
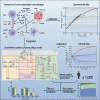
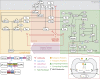
Quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) modeling is an emerging mechanistic computational approach that couples drug pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics and the course of disease progression. It has begun to play important roles in drug development for complex diseases such as cancer, including triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The combination of the anti-PD-L1 antibody atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel has shown clinical activity in advanced TNBC with PD-L1-positive tumor-infiltrating immune cells. As tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) serve as major contributors to the immuno-suppressive tumor microenvironment, we incorporated the dynamics of TAMs into our previously published QSP model to investigate their impact on cancer treatment. We show that through proper calibration, the model captures the macrophage heterogeneity in the tumor microenvironment while maintaining its predictive power of the trial results at the population level. Despite its high mechanistic complexity, the modularized QSP platform can be readily reproduced, expanded for new species of interest, and applied in clinical trial simulation.
Keywords: Biophysics; Cancer; Immunology; Pharmacology.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Emens has had research funding from Genentech, F Hoffman La Roche, EMD Serono, Merck, AstraZeneca, Tempest, Bolt, Silverback, Takeda, CytomX, Compugen, Abbvie, BMS, Next Cure, Immune Onc. She has served as a paid consultant for, F Hoffman La Roche, Genentech, Macrogenics, Lilly, Chug, Silverback, Shionogi, CytomX, GPCR, Immunitas, DNAMx, Gilead, and Mersana. Dr. Emens also has an executive role at the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer and has ownership interest in Molecuvax. Dr. Popel is a consultant to AsclepiX Therapeutics and CytomX Therapeutics. He receives research funding from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, CytomX Therapeutics. Dr Cesar Santa-Maria has research funding from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb and has served on advisory boards for Bristol Meyers Squibb, Genomic Health, Seattle Genetics, Athenex, Halozyme and Polyphor. The terms of these arrangements are being managed by the Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Dr. Santa-Maria has research funding from Pfizer, Astrazeneca, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb and has served on advisory boards for Bristol Meyers Squibb, Genomic Health, Seattle Genetics, Athenex, Halozyme and Polyphor.
Figures





References
-
- Anders C.K., Carey L.A. In: ER/PR negative, HER2-negative (triple-negative) breast cancer. Hayes D.F., Burstein H.J., editors. UpToDate; 2022.
-
- Autenshlyus A., Arkhipov S., Mikhaylova E., Marinkin I., Arkhipova V., Varaksin N., Vavilin V., Lyahovich V. Analyzing the relationship between the cytokine profile of invasive breast carcinoma, its histopathological characteristics and metastasis to regional lymph nodes. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:11359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90930-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

