Two-stage hybrid network for segmentation of COVID-19 pneumonia lesions in CT images: a multicenter study
- PMID: 35856130
- PMCID: PMC9294771
- DOI: 10.1007/s11517-022-02619-8
Two-stage hybrid network for segmentation of COVID-19 pneumonia lesions in CT images: a multicenter study
Abstract
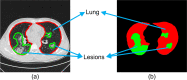
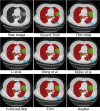
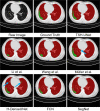
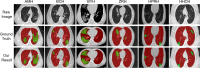
COVID-19 has been spreading continuously since its outbreak, and the detection of its manifestations in the lung via chest computed tomography (CT) imaging is essential to investigate the diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 as an indispensable step. Automatic and accurate segmentation of infected lesions is highly required for fast and accurate diagnosis and further assessment of COVID-19 pneumonia. However, the two-dimensional methods generally neglect the intraslice context, while the three-dimensional methods usually have high GPU memory consumption and calculation cost. To address these limitations, we propose a two-stage hybrid UNet to automatically segment infected regions, which is evaluated on the multicenter data obtained from seven hospitals. Moreover, we train a 3D-ResNet for COVID-19 pneumonia screening. In segmentation tasks, the Dice coefficient reaches 97.23% for lung segmentation and 84.58% for lesion segmentation. In classification tasks, our model can identify COVID-19 pneumonia with an area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve value of 0.92, an accuracy of 92.44%, a sensitivity of 93.94%, and a specificity of 92.45%. In comparison with other state-of-the-art methods, the proposed approach could be implemented as an efficient assisting tool for radiologists in COVID-19 diagnosis from CT images.
Keywords: COVID-19; Computed tomography; Infected lesion segmentation; Screening.
© 2022. International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
From community-acquired pneumonia to COVID-19: a deep learning-based method for quantitative analysis of COVID-19 on thick-section CT scans.Eur Radiol. 2020 Dec;30(12):6828-6837. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07042-x. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32683550 Free PMC article.
-
CAD systems for COVID-19 diagnosis and disease stage classification by segmentation of infected regions from CT images.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Jul 6;23(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04818-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35794537 Free PMC article.
-
CARes-UNet: Content-aware residual UNet for lesion segmentation of COVID-19 from chest CT images.Med Phys. 2021 Nov;48(11):7127-7140. doi: 10.1002/mp.15231. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34528263 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 30;9:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. PMID: 32997361 Updated.
-
Radiological perspective of COVID-19 pneumonia: The early features and progressive behaviour on high-resolution CT.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021 Apr;65(2):208-212. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13139. Epub 2021 Jan 24. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33491340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Robust Medical Diagnosis: A Novel Two-Phase Deep Learning Framework for Adversarial Proof Disease Detection in Radiology Images.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Feb;37(1):308-338. doi: 10.1007/s10278-023-00916-8. Epub 2024 Jan 10. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38343214 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2019YFC0118100/the National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2017YFA0700401/the National Key Research and Development Program of China
- No.2020FCA015/Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Key Project of Science and Technology of Hubei Province
- 81671851/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81827808/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 61936013/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Z211100003521003/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81571836/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018167/CAS Youth Innovation Promotion Association under Grant
- Zhuhai HLHPTP201703/High-Level Talents Team Introduction in Zhuhai City
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

