RRM2 enhances MYCN-driven neuroblastoma formation and acts as a synergistic target with CHK1 inhibition
- PMID: 35857500
- PMCID: PMC9278860
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abn1382
RRM2 enhances MYCN-driven neuroblastoma formation and acts as a synergistic target with CHK1 inhibition
Abstract
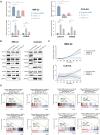
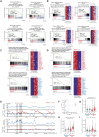
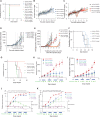
High-risk neuroblastoma, a pediatric tumor originating from the sympathetic nervous system, has a low mutation load but highly recurrent somatic DNA copy number variants. Previously, segmental gains and/or amplifications allowed identification of drivers for neuroblastoma development. Using this approach, combined with gene dosage impact on expression and survival, we identified ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 (RRM2) as a candidate dependency factor further supported by growth inhibition upon in vitro knockdown and accelerated tumor formation in a neuroblastoma zebrafish model coexpressing human RRM2 with MYCN. Forced RRM2 induction alleviates excessive replicative stress induced by CHK1 inhibition, while high RRM2 expression in human neuroblastomas correlates with high CHK1 activity. MYCN-driven zebrafish tumors with RRM2 co-overexpression exhibit differentially expressed DNA repair genes in keeping with enhanced ATR-CHK1 signaling activity. In vitro, RRM2 inhibition enhances intrinsic replication stress checkpoint addiction. Last, combinatorial RRM2-CHK1 inhibition acts synergistic in high-risk neuroblastoma cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models, illustrating the therapeutic potential.
Figures






References
-
- Jansky S., Sharma A. K., Korber V., Quintero A., Toprak U. H., Wecht E. M., Gartlgruber M., Greco A., Chomsky E., Grunewald T. G. P., Henrich K. O., Tanay A., Herrmann C., Hofer T., Westermann F., Single-cell transcriptomic analyses provide insights into the developmental origins of neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 53, 683–693 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Kameneva P., Artemov A. V., Kastriti M. E., Faure L., Olsen T. K., Otte J., Erickson A., Semsch B., Andersson E. R., Ratz M., Frisen J., Tischler A. S., de Krijger R. R., Bouderlique T., Akkuratova N., Vorontsova M., Gusev O., Fried K., Sundstrom E., Mei S., Kogner P., Baryawno N., Kharchenko P. V., Adameyko I., Single-cell transcriptomics of human embryos identifies multiple sympathoblast lineages with potential implications for neuroblastoma origin. Nat. Genet. 53, 694–706 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peifer M., Hertwig F., Roels F., Dreidax D., Gartlgruber M., Menon R., Krämer A., Roncaioli J. L., Sand F., Heuckmann J. M., Ikram F., Schmidt R., Ackermann S., Engesser A., Kahlert Y., Vogel W., Altmüller J., Nürnberg P., Thierry-Mieg J., Thierry-Mieg D., Mariappan A., Heynck S., Mariotti E., Henrich K.-O., Gloeckner C., Bosco G., Leuschner I., Schweiger M. R., Savelyeva L., Watkins S. C., Shao C., Bell E., Höfer T., Achter V., Lang U., Theissen J., Volland R., Saadati M., Eggert A., de Wilde B., Berthold F., Peng Z., Zhao C., Shi L., Ortmann M., Büttner R., Perner S., Hero B., Schramm A., Schulte J. H., Herrmann C., O’Sullivan R. J., Westermann F., Thomas R. K., Fischer M., Telomerase activation by genomic rearrangements in high-risk neuroblastoma. Nature 526, 700–704 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koche R. P., Rodriguez-Fos E., Helmsauer K., Burkert M., MacArthur I. C., Maag J., Chamorro R., Munoz-Perez N., Puiggròs M., Garcia H. D., Bei Y., Röefzaad C., Bardinet V., Szymansky A., Winkler A., Thole T., Timme N., Kasack K., Fuchs S., Klironomos F., Thiessen N., Blanc E., Schmelz K., Künkele A., Hundsdörfer P., Rosswog C., Theissen J., Beule D., Deubzer H., Sauer S., Toedling J., Fischer M., Hertwig F., Schwarz R. F., Eggert A., Torrents D., Schulte J. H., Henssen A. G., Extrachromosomal circular DNA drives oncogenic genome remodeling in neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 52, 29–34 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

