ZAKα-driven ribotoxic stress response activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome
- PMID: 35857590
- PMCID: PMC7614315
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abl6324
ZAKα-driven ribotoxic stress response activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome
Abstract
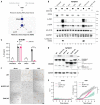
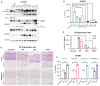
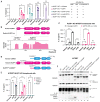
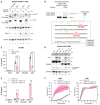
Human NLRP1 (NACHT, LRR, and PYD domain-containing protein 1) is an innate immune sensor predominantly expressed in the skin and airway epithelium. Here, we report that human NLRP1 senses the ultraviolet B (UVB)- and toxin-induced ribotoxic stress response (RSR). Biochemically, RSR leads to the direct hyperphosphorylation of a human-specific disordered linker region of NLRP1 (NLRP1DR) by MAP3K20/ZAKα kinase and its downstream effector, p38. Mutating a single ZAKα phosphorylation site in NLRP1DR abrogates UVB- and ribotoxin-driven pyroptosis in human keratinocytes. Moreover, fusing NLRP1DR to CARD8, which is insensitive to RSR by itself, creates a minimal inflammasome sensor for UVB and ribotoxins. These results provide insight into UVB sensing by human skin keratinocytes, identify several ribotoxins as NLRP1 agonists, and establish inflammasome-driven pyroptosis as an integral component of the RSR.
Conflict of interest statement
S.L.M. is a scientific advisor for Odyssey therapeutics and NRG therapeutics. J.E.C. is a member of the Board of Directors, 3T Biosciences and Chief Scientific Officer of Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy. F.L.Z., K.S.R., T.G.A., S.Z. are co-inventors of a patent (PCT/SG2022/050086) based on this work.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

