Mistletoes could moderate drought impacts on birds, but are themselves susceptible to drought-induced dieback
- PMID: 35858071
- PMCID: PMC9277258
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2022.0358
Mistletoes could moderate drought impacts on birds, but are themselves susceptible to drought-induced dieback
Abstract
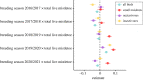
Mistletoes are hemiparasitic plants and keystone species in many ecosystems globally. Given predicted increases in drought frequency and intensity, mistletoes may be crucial for moderating drought impacts on community structure. Dependent on host vascular flows, mistletoes can succumb to stress when water availability falls, making them susceptible to mortality during drought. We counted mistletoe across greater than 350 000 km2 of southeastern Australia and conducted standardized bird surveys between 2016 and 2021, spanning a major drought event in 2018-2019. We aimed to identify predictors of mistletoe abundance and mortality and determine whether mistletoes might moderate drought impacts on woodland birds. Live mistletoe abundance varied with tree species composition, land use and presence of mistletoebirds. Mistletoe mortality was widespread, consistent with high 2018/2019 summer temperatures, low 2019/2020 summer rainfall and the interaction between summer temperatures and rainfall in 2019/2020. The positive association between surviving mistletoes and woodland birds was greatest in the peak drought breeding seasons of 2018/2019 and 2019/2020, particularly for small residents and insectivores. Paradoxically, mistletoes could moderate drought impacts on birds, but are themselves vulnerable to drought-induced mortality. An improved understanding of the drivers and dynamics of mistletoe mortality is needed to address potential cascading trophic impacts associated with mistletoe die-off.
Keywords: climate change; ecosystem resillience; food webs; global change; phenology; population monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Watson DM. 2001. Mistletoe—a keystone resource in forests and woodlands worldwide. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 32, 219-249. ( 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114024) - DOI
-
- Griebel A, Watson D, Pendall E. 2017. Mistletoe, friend and foe: synthesizing ecosystem implications of mistletoe infection. Environ. Res. Lett. 12, 115012. ( 10.1088/1748-9326/aa8fff) - DOI
-
- Fonturbel FE, Lara A, Lobos D, Little C. 2018. The cascade impacts of climate change could threaten key ecological interactions. Ecosphere 9, e02485. ( 10.1002/ecs2.2485) - DOI
-
- Fontúrbel FE, Nespolo RF, Amico GC, Watson DM. 2021. Climate change can disrupt ecological interactions in mysterious ways: using ecological generalists to forecast community-wide effects. Clim. Change Ecol. 2, 100044. ( 10.1016/j.ecochg.2021.100044) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
