Combinatorial approaches for treating neuropsychiatric social impairment
- PMID: 35858103
- PMCID: PMC9274330
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0051
Combinatorial approaches for treating neuropsychiatric social impairment
Abstract
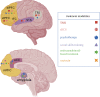
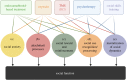
Social behaviour is an essential component of human life and deficits in social function are seen across multiple psychiatric conditions with high morbidity. However, there are currently no FDA-approved treatments for social dysfunction. Since social cognition and behaviour rely on multiple signalling processes acting in concert across various neural networks, treatments aimed at social function may inherently require a combinatorial approach. Here, we describe the social neurobiology of the oxytocin and endocannabinoid signalling systems as well as translational evidence for their use in treating symptoms in the social domain. We leverage this systems neurobiology to propose a network-based framework that involves pharmacology, psychotherapy, non-invasive brain stimulation and social skills training to combinatorially target trans-diagnostic social impairment. Lastly, we discuss the combined use of oxytocin and endocannabinoids within our proposed framework as an illustrative strategy to treat specific aspects of social function. Using this framework provides a roadmap for actionable treatment strategies for neuropsychiatric social impairment. This article is part of the theme issue 'Interplays between oxytocin and other neuromodulators in shaping complex social behaviours'.
Keywords: combinatorial; endocannabinoids; oxytocin; social behaviour; social cognition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex-specific and social experience-dependent oxytocin-endocannabinoid interactions in the nucleus accumbens: implications for social behaviour.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210057. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0057. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between the oxytocin and opioid systems in regulating social behaviour.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210050. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0050. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of oxytocin in shaping complex social behaviours: possible interactions with other neuromodulators.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210058. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0058. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin-a social peptide? Deconstructing the evidence.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210055. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0055. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin and microglia in the development of social behaviour.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210059. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0059. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxytocin does not stand alone.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210047. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0047. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858106 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dissecting social decision-making: A spotlight on oxytocinergic transmission.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Dec 22;15:1061934. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1061934. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36618824 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

