FBXW24 controls female meiotic prophase progression by regulating SYCP3 ubiquitination
- PMID: 35858239
- PMCID: PMC9299759
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.891
FBXW24 controls female meiotic prophase progression by regulating SYCP3 ubiquitination
Abstract
Background: An impeccable female meiotic prophase is critical for producing a high-quality oocyte and, ultimately, a healthy newborn. SYCP3 is a key component of the synaptonemal complex regulating meiotic homologous recombination. However, what regulates SYCP3 stability is unknown.
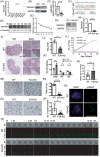
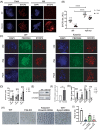
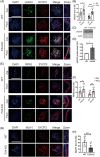
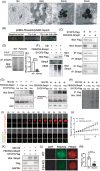
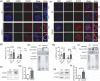
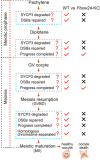
Methods: Fertility assays, follicle counting, meiotic prophase stage (leptotene, zygotene, pachytene and diplotene) analysis and live imaging were employed to examine how FBXW24 knockout (KO) affect female fertility, follicle reserve, oocyte quality, meiotic prophase progression of female germ cells, and meiosis of oocytes. Western blot and immunostaining were used to examined the levels & signals (intensity, foci) of SYCP3 and multiple key DSB indicators & repair proteins (γH2AX, RPA2, p-CHK2, RAD51, MLH1, HORMAD1, TRIP13) after FBXW24 KO. Co-IP and immuno-EM were used to examined the interaction between FBXW24 and SYCP3; Mass spec was used to characterize the ubiquitination sites in SYCP3; In vivo & in vitro ubiquitination assays were utilized to determine the key sites in SYCP3 & FBXW24 for ubiquitination.
Results: Fbxw24-knockout (KO) female mice were infertile due to massive oocyte death upon meiosis entry. Fbxw24-KO oocytes were defective due to elevated DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and inseparable homologous chromosomes. Fbxw24-KO germ cells showed increased SYCP3 levels, delayed prophase progression, increased DSBs, and decreased crossover foci. Next, we found that FBXW24 directly binds and ubiquitinates SYCP3 to regulate its stability. In addition, several key residues important for SYCP3 ubiquitination and FBXW24 ubiquitinating activity were characterized.
Conclusions: We proposed that FBXW24 regulates the timely degradation of SYCP3 to ensure normal crossover and DSB repair during pachytene. FBXW24-KO delayed SYCP3 degradation and DSB repair from pachytene until metaphase II (MII), ultimately causing failure in oocyte maturation, oocyte death, and infertility.
Keywords: FBXW24; SYCP3; meiotic prophase; oocyte; ubiquitination.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Miyamoto T, Hasuike S, Yogev L, et al. Azoospermia in patients heterozygous for a mutation in SYCP3. Lancet. 2003;362(9397):1714‐1719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
