Development and Validation of a Neonatal Physical Maturity Score for Low- and Middle-Income Countries
- PMID: 35858649
- PMCID: PMC11105931
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1905-5334
Development and Validation of a Neonatal Physical Maturity Score for Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Abstract
Objective: Currently available gestational age scoring systems are complex and inaccurate for wider use in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC), particularly in infants with neonatal encephalopathy. Here, we aimed to develop a scoring system based on physical characteristics for identifying late preterm infants from term infants.
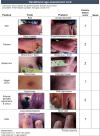
Study design: This was a prospective observational study conducted in 2 phases- the discovery phase and validation phase. In the first phase, we examined the accuracy of 10 objective physical characteristics in a prospective cohort of 1,006 infants recruited from three hospitals in South India. A weighted scoring system and a photo card were then developed based on the six best performing characteristics which were validated in another prospective cohort of 1,004 infants.
Results: The final score had a sensitivity of 66.0% (95% confidence intervals [CIs], 58.4-73.8%), specificity of 80.0% (95% CI, 77.2-82.7%), and a negative predictive value of 93.0% (95% CI, 90.5-94.5%).
Conclusion: This scoring system may have wider applications in LMIC, particularly in community settings and in infants with neonatal encephalopathy.
Key points: · This is an easily administered scoring system using physical characters to identify late preterm infants.. · The scoring is not affected by neurological injury and can be used in encephalopathic infants.. · Overall accuracy is better than previous scores encompassing the physical criteria alone..
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Ballard J L, Khoury J C, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman B L, Lipp R. New Ballard score, expanded to include extremely premature infants. J Pediatr. 1991;119(03):417–423. - PubMed
-
- Dubowitz L M, Dubowitz V, Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970;77(01):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Lee A C, Panchal P, Folger L et al.Diagnostic accuracy of neonatal assessment for gestational age determination: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2017;140(06):e20171423. - PubMed