Evaluation of a novel multiplex qPCR method for rapid detection and quantification of pathogens associated with calf diarrhoea
- PMID: 35858716
- PMCID: PMC9796748
- DOI: 10.1111/jam.15722
Evaluation of a novel multiplex qPCR method for rapid detection and quantification of pathogens associated with calf diarrhoea
Abstract
Aims: Diarrhoea is a common health problem in calves and a main reason for use of antimicrobials. It is associated with several bacterial, viral and parasitic pathogens, most of which are commonly present in healthy animals. Methods, which quantify the causative agents, may therefore improve confidence in associating a pathogen to the disease. This study evaluated a novel commercially available, multiplex quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay (Enterit4Calves) for detection and quantification of pathogens associated with calf-diarrhoea.
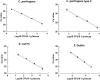
Methods and results: Performance of the method was first evaluated under laboratory conditions. Then it was compared with current routine methods for detection of pathogens in faecal samples from 65 calves with diarrhoea and in 30 spiked faecal samples. The qPCR efficiencies were between 84%-103% and detection limits of 100-1000 copies of nucleic acids per sample were observed. Correct identification was obtained on 42 strains of cultured target bacteria, with only one false positive reaction from 135 nontarget bacteria. Kappa values for agreement between the novel assay and current routine methods varied between 0.38 and 0.83.
Conclusion: The novel qPCR method showed good performance under laboratory conditions and a fair to good agreement with current routine methods when used for testing of field samples.
Significance and impact of study: In addition to having fair to good detection abilities, the novel qPCR method allowed quantification of pathogens. In the future, use of quantification may improve diagnosis and hence treatment of calf diarrhoea.
Keywords: Calf diarrhoea; calf scours; detection; multiplex qPCR; quantification.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Applied Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for Applied Microbiology.
Conflict of interest statement
P. Pansri is an employee of the company DNA‐diagnostic A/S, which produces and sells the assays evaluated in the current study. The remaining authors declare that they do not have any financial or personal relationships that could inappropriately influence or bias the content of the paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of novel multiplex qPCR assays for diagnosis of pathogens associated with the bovine respiratory disease complex.Vet J. 2020 Feb;256:105425. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2020.105425. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Vet J. 2020. PMID: 32113583 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for rapid detection of 9 pathogens directly from stools of travelers with diarrhea.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1300-1307.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.03.037. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23639597
-
A novel multiplex RT-qPCR assay for simultaneous detection of bovine norovirus, torovirus, and kobuvirus in fecal samples from diarrheic calves.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2023 Nov;35(6):742-750. doi: 10.1177/10406387231191723. Epub 2023 Aug 12. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2023. PMID: 37571922 Free PMC article.
-
Development and performance evaluation of calf diarrhea pathogen nucleic acid purification and detection workflow.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012 Sep;24(5):945-53. doi: 10.1177/1040638712456976. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012. PMID: 22914823
-
Efficacy of Molecular Methods for the Diagnosis of Enteropathogenic Microorganisms Associated with Diarrhoea: A Systematic Review.J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2024 Dec 28;33(4):552-562. doi: 10.15403/jgld-5653. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2024. PMID: 39733307
Cited by
-
Simultaneous detection of seven bacterial pathogens transmitted by flies using the reverse line blot hybridization assay.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Feb 22;17(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13071-024-06170-3. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38389104 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and epidemiological investigation of a dual fluorescent qPCR assay for Pasteurella multocida and Salmonella in yaks in the Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture of Garzê, China.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 4;15:1599817. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1599817. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40535542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuelo, A. (2016) Investigation of an outbreak of neonatal calf diarrhoea in a dairy herd. Veterinary Record Case Reports, 4, 10.1136.
-
- Broeders, S. , Huber, I. , Grohmann, L. , Berben, G. , Taverniers, I. , Mazzara, M. et al. (2014) Guidelines for validation of qualitative real‐time PCR methods. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 37, 115–126.
-
- Buzard, G.S. , Baker, D. , Wolcott, M.J. , Norwood, D.A. & Dauphin, L.A. (2010) Multi‐platform comparison of ten commercial master mixes for probe‐based real‐time polymerase chain reaction detection of bioterrorism threat agents for surge preparedness. Forensic Science International, 223, 292–297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

