CircGPR137B/miR-4739/FTO feedback loop suppresses tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35858900
- PMCID: PMC9297645
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01619-4
CircGPR137B/miR-4739/FTO feedback loop suppresses tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence indicates that circular RNAs (circRNAs) and m6A RNA methylation participate in the pathogenesis and metastasis of multiple malignancies including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, it remains undocumented how circRNAs form a feedback loop with the m6A modification contributing to HCC.
Methods: A novel hsa_circ_0017114 (circGPR137B) was identified from three pairs of primary HCC and adjacent normal tissues by circRNA expression profiling. The association of circGPR137B and miR-4739 with clinicopathological parameters and prognosis in patients with HCC was analyzed by RT-qPCR, fluorescence in situ hybridization and TCGA cohorts. The role of circGPR137B in HCC was estimated in vitro and in vivo. RT-qPCR, western blot, m6A dot blot, RIP, MeRIP and dual-luciferase reporter assays were used to validate the reciprocal regulation of the feedback loop among circGPR137B, miR-4739 and m6A demethylase FTO. Meanwhile, the expression, function and prognosis of FTO in HCC were investigated by RT-qPCR, western blot, TCGA and rescue experiments.
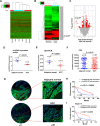
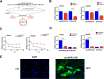
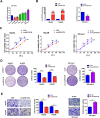
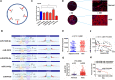
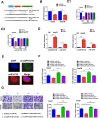
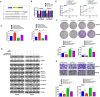
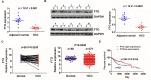
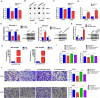
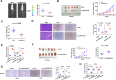
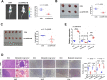
Results: We identified a new dramatically downregulated circGPR137B in HCC tissues, and found that downregulation of circGPR137B or upregulation of miR-4739 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with HCC. Ectopic expression of circGPR137B strikingly repressed the proliferation, colony formation and invasion, whereas knockdown of circGPR137B harbored the opposite effects. Moreover, restored expression of circGPR137B inhibited tumor growth and lung metastasis in vivo. Further investigations showed that circGPR137B, co-localized with miR-4739 in the cytoplasm, acted as a sponge for miR-4739 to upregulate its target FTO, which mediated m6A demethylation of circGPR137B and promoted its expression. Thus, a feedback loop comprising circGPR137B/miR-4739/FTO axis was formed. FTO suppressed cell growth and indicated favorable survival in patients with HCC.
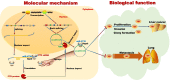
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that circGPR137B inhibits HCC tumorigenesis and metastasis through the circGPR137B/miR-4739/FTO feedback loop. This positive feedback mechanism executed by functional coupling between a circRNA sponge and an m6A modification event suggests a model for epigenetics.
Keywords: CircGPR137B; Demethylation; FTO; Hepatocellular carcinoma; m6A; miR-4739.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
m6A-modification regulated circ-CCT3 acts as the sponge of miR-378a-3p to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Epigenetics. 2023 Dec;18(1):2204772. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2204772. Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37092305 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0072309 promotes tumorigenesis and invasion by regulating the miR-607/FTO axis in non-small cell lung carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 20;13(8):11629-11645. doi: 10.18632/aging.202856. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33879631 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification of circular RNA circASH2L suppresses growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating hsa-miR-525-3p/MTUS2 axis.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 14;22(1):1026. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05745-z. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39543614 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-CSPP1 knockdown suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression through miR-493-5p releasing-mediated HMGB1 downregulation.Cell Signal. 2021 Oct;86:110065. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110065. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Cell Signal. 2021. PMID: 34182091 Review.
-
RNA methylations in depression, from pathological mechanism to therapeutic potential.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Sep;215:115750. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115750. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37595670 Review.
Cited by
-
CypA/TAF15/STAT5A/miR-514a-3p feedback loop drives ovarian cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2024 Nov;43(49):3570-3585. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03188-w. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39402372
-
Non-coding RNA methylation modifications in hepatocellular carcinoma: interactions and potential implications.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec 18;21(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01357-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38111040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New understandings of the genetic regulatory relationship between non-coding RNAs and m6A modification.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 6;14:1270983. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1270983. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38125749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircHLA-C: A significantly upregulated circRNA co-existing in oral leukoplakia and oral lichen planus.Organogenesis. 2023 Dec 31;19(1):2234504. doi: 10.1080/15476278.2023.2234504. Organogenesis. 2023. PMID: 37531467 Free PMC article.
-
Potential involvement of cuproptosis induced by m6A-modified autophagy gene ATG10 in KICH : Cuproptosis induced by m6A-modified ATG10 in KICH.BMC Cancer. 2024 Dec 30;24(1):1591. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13300-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39736548 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

