APOA1 mRNA and protein in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma correlate with the disease outcome
- PMID: 35858961
- PMCID: PMC9300670
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16434-6
APOA1 mRNA and protein in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma correlate with the disease outcome
Abstract
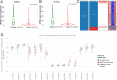
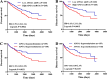
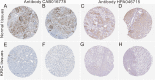
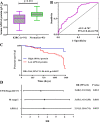
Renal cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors with high mortality, and kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) is the most common type of renal cancer. We attempted to evaluate the clinical and prognostic significance of Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) mRNA and protein in KIRC patients. Clinical data along with RNA-sequencing data were downloaded from UCSC Xena. The Human Protein Atlas database was searched to reveal APOA1 protein expression profiles in KIRC and normal renal tissues. The TIMER database was applied to determine the correlations of APOA1 with immune cells and PD-1 and PD-L1 in KIRC. Ninety-one cases of KIRC patients and 93 healthy controls from our hospital were enrolled for clinical validation. Levels of APOA1 mRNA in KIRC tissues (N = 535) are not only lower than the levels in normal renal tissues (N = 117), but also in paired normal renal tissues (N = 72). High expression of APOA1 mRNA at the time of surgery was correlated with worse overall survival (OS) (HR 1.66; p = 0.037) and disease-free survival (DFS) (HR 1.65; p = 0.047), and APOA1 DNA methylation was linked to worse OS (HR 2.1; p = 0.001) rather than DFS (HR 1.12; p = 0.624) in KIRC patients. Concentrations of preoperative serum APOA1 protein were markedly decreased in KIRC patients compared to healthy controls (p < 0.01), and low levels of APOA1 protein predicted less favorable OS than those with high levels (HR = 2.84, p = 0.0407). APOA1 negatively correlated with various immune cell infiltrates and PD-L1 expression (r = - 0.283, p = 2.74e-11) according to the TIMER database. Low levels of APOA1 mRNA at the time of surgery predict favorable survival in KIRC patients. Our results provide insights to identify a novel prognostic index with great clinical utility.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulated Transcription Factor PITX1 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma-Based Bioinformatic Analysis and Experimental Verification.Dis Markers. 2021 Nov 23;2021:7694239. doi: 10.1155/2021/7694239. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34868397 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive investigation discovered the novel methyltransferase METTL24 as one presumably prognostic gene for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma potentially modulating tumor immune microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 14;13:926461. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.926461. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311770 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation between methylation of interferon regulatory factor 6 gene promoter in renal tissues and overall survival of patients with Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 10;41(2):150-156. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20220921-00635. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38311552 Chinese.
-
Downregulation of RAB17 have a poor prognosis in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and its expression correlates with DNA methylation and immune infiltration.Cell Signal. 2023 Sep;109:110743. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110743. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Cell Signal. 2023. PMID: 37269962
-
Association between PD-L1 Expression and the Prognosis and Clinicopathologic Features of Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Urol Int. 2020;104(7-8):533-541. doi: 10.1159/000506296. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Urol Int. 2020. PMID: 32623437
Cited by
-
Low serum apolipoprotein A1 level predicts poor prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the real world: a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jan 12;24(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11818-5. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38212711 Free PMC article.
-
APOA1 mRNA and serum APOA1 protein as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 May 31;13(5):2141-2154. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1966. Epub 2024 May 23. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38881912 Free PMC article.
-
APOA1 promotes tumor proliferation and migration and may be a potential pan-cancer biomarker and immunotherapy target.Transl Oncol. 2025 May;55:102344. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102344. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40088749 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Apolipoprotein A1 Expression Correlates with Tumor-Associated Neutrophils and T Lymphocytes in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 7;46(3):2155-2165. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030139. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534755 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of the bisphenol A affected kidney in mice.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 24;10:1260716. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1260716. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38074096 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

