Application of artificial intelligence-based dual-modality analysis combining fundus photography and optical coherence tomography in diabetic retinopathy screening in a community hospital
- PMID: 35859144
- PMCID: PMC9301845
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-022-01018-2
Application of artificial intelligence-based dual-modality analysis combining fundus photography and optical coherence tomography in diabetic retinopathy screening in a community hospital
Abstract
Background: To assess the feasibility and clinical utility of artificial intelligence (AI)-based screening for diabetic retinopathy (DR) and macular edema (ME) by combining fundus photos and optical coherence tomography (OCT) images in a community hospital.
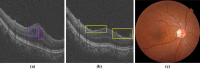
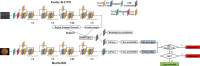
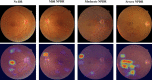
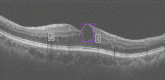
Methods: Fundus photos and OCT images were taken for 600 diabetic patients in a community hospital. Ophthalmologists graded these fundus photos according to the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy (ICDR) Severity Scale as the ground truth. Two existing trained AI models were used to automatically classify the fundus images into DR grades according to ICDR, and to detect concomitant ME from OCT images, respectively. The criteria for referral were DR grades 2-4 and/or the presence of ME. The sensitivity and specificity of AI grading were evaluated. The number of referable DR cases confirmed by ophthalmologists and AI was calculated, respectively.
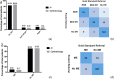
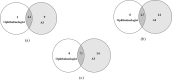
Results: DR was detected in 81 (13.5%) participants by ophthalmologists and in 94 (15.6%) by AI, and 45 (7.5%) and 53 (8.8%) participants were diagnosed with referable DR by ophthalmologists and by AI, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve (AUC) of AI for detecting DR were 91.67%, 96.92% and 0.944, respectively. For detecting referable DR, the sensitivity, specificity and AUC of AI were 97.78%, 98.38% and 0.981, respectively. ME was detected from OCT images in 49 (8.2%) participants by ophthalmologists and in 57 (9.5%) by AI, and the sensitivity, specificity and AUC of AI were 91.30%, 97.46% and 0.944, respectively. When combining fundus photos and OCT images, the number of referrals identified by ophthalmologists increased from 45 to 75 and from 53 to 85 by AI.
Conclusion: AI-based DR screening has high sensitivity and specificity and may feasibly improve the referral rate of community DR.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Diabetic retinopathy; Optical coherence tomography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no proprietary or commercial interest in any materials discussed in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence-based screening for diabetic retinopathy at community hospital.Eye (Lond). 2020 Mar;34(3):572-576. doi: 10.1038/s41433-019-0562-4. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Eye (Lond). 2020. PMID: 31455902 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 21 artificial intelligence algorithms in automated diabetic retinopathy screening using handheld fundus camera.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2352018. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2352018. Epub 2024 May 13. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 38738798 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of Artificial Intelligence Algorithm in the Detection and Staging of Diabetic Retinopathy through Fundus Photography: An Automated Tool for Detection and Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep 25;28(2):81-86. doi: 10.4103/meajo.meajo_406_20. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34759664 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Diabetic Macular Edema From Fundus Photography and Optical Coherence Tomography Images: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Diabetes Care. 2024 Feb 1;47(2):304-319. doi: 10.2337/dc23-0993. Diabetes Care. 2024. PMID: 38241500
-
Advancing Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis: Leveraging Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging with Convolutional Neural Networks.Rom J Ophthalmol. 2023 Oct-Dec;67(4):398-402. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2023.63. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38239418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fundus Image Deep Learning Study to Explore the Association of Retinal Morphology with Age-Related Macular Degeneration Polygenic Risk Score.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 13;12(9):2092. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092092. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335605 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of artificial intelligence in diabetic retinopathy screening: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025 Apr 22;11(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40942-025-00670-9. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025. PMID: 40264218 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence system for screening multiple fundus diseases in Chinese primary healthcare settings: a real-world, multicentre and cross-sectional study of 4795 cases.Br J Ophthalmol. 2024 Feb 21;108(3):424-431. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2022-322940. Br J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 36878715 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid deep learning models for the screening of Diabetic Macular Edema in optical coherence tomography volumes.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 31;14(1):17633. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68489-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39085461 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal vascular arcade angle as a biomarker for visual improvement after epiretinal membrane surgery.Eye (Lond). 2024 Mar;38(4):778-785. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02776-6. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 37865724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leasher JL, Bourne RR, Flaxman SR, Jonas JB, Keeffe J, Naidoo K, Pesudovs K, Price H, White RA, Wong TY, et al. Global estimates on the number of people blind or visually impaired by diabetic retinopathy: a meta-analysis from 1990 to 2010. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(9):1643–1649. doi: 10.2337/dc15-2171. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2020SBYMZB01/Shanghai Jing'an District Shibei Hospital Research Project Grant
- 2020QN05/Project of Shanghai Jing'an District Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning
- 2019SY012/Advanced and Appropriate Technology Promotion Project of Shanghai Health Commission
- 2018YFA0701700/National Key R&D Program of China under Grant
- ZK2019B27/Shanghai Medical Key Special Construction Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

