The Effect of Growth Hormone Therapy on Cardiac Outcomes in Noonan Syndrome: Long Term Follow-up Results
- PMID: 35859537
- PMCID: PMC9724055
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2022.2022-12-13
The Effect of Growth Hormone Therapy on Cardiac Outcomes in Noonan Syndrome: Long Term Follow-up Results
Abstract
Objective: Cardiac involvement is common in Noonan syndrome (NS). Concerns have been raised regarding the effect of recombinant growth hormone (rGH) use on ventricular wall thickness and a possible increased risk of cardiac side effects. This study aimed to investigate the effect of rGH on the development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and other cardiac findings in NS.
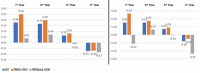
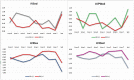
Methods: Patients under the age of 18 years and diagnosed with NS according to the Van der Burgt criteria, were included. Patients were divided into two groups according to those receiving rGH or not at the time of obtaining cardiac measurements. Before and after the treatment, electrocardiographic and echocardiographic (ECHO) assessments were made, including interventricular septal thickness, left ventricular internal diameter, and left ventricular posterior thickness. Results were expressed as Z scores.
Results: Twenty-four NS subjects (16 boys, eight girls) were included. At the beginning of the follow up, the overall height standard deviation score was -2.56±0.94. Sixteen were on rGH. The mean rGH treatment duration was 8.3±3.8 years, and the mean dose was 0.22±0.04 mg/kg/week. The final height was 169±8.2 cm, and 10 of 11 patients who reached the final height received rGH. There was no difference between the rGH and non-rGH groups in terms of ECHO parameters pre-and post-treatment.
Conclusion: In this cohort, there was no change in ECHO parameters on rGH and during follow-up. These results suggest that rGH is safe in NS patients with cardiac pathology under close follow-up.
Keywords: Noonan syndrome; Recombinant growth hormone therapy; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; left ventricular dimension.
Figures
References
-
- Malaquias AC, Jorge AAL. Activation of the MAPK pathway (RASopathies) and partial growth hormone insensitivity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;513:111040. - PubMed
-
- Ranke MB, Heidemann P, Knupfer C, Enders H, Schmaltz AA, Bierich JR. Noonan syndrome: growth and clinical manifestations in 144 cases. Eur J Pediatr. 1988;148:220–227. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner RN, Roche AF, Himes JH. Incremental growth tables: supplementary to previously published charts. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986;43:711–722. - PubMed
-
- Tartaglia M, Mehler EL, Goldberg R, Zampino G, Brunner HG, Kremer H, van der Burgt I, Crosby AH, Ion A, Jeffery S, Kalidas K, Patton MA, Kucherlapati RS, Gelb BD. Mutations in PTPN11, encoding the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2, cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2001;29:465–468. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
